+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Evolutionary compaction and adaptation visualized by the structure of the dormant microsporidian ribosome. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Microbiol, Vol. 4, Issue 11, Page 1798-1804, Year 2019 |
| Publish date | Jul 22, 2019 |
 Authors Authors | Jonas Barandun / Mirjam Hunziker / Charles R Vossbrinck / Sebastian Klinge /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Microsporidia are eukaryotic parasites that infect essentially all animal species, including many of agricultural importance, and are significant opportunistic parasites of humans. They are ...Microsporidia are eukaryotic parasites that infect essentially all animal species, including many of agricultural importance, and are significant opportunistic parasites of humans. They are characterized by having a specialized infection apparatus, an obligate intracellular lifestyle, rudimentary mitochondria and the smallest known eukaryotic genomes. Extreme genome compaction led to minimal gene sizes affecting even conserved ancient complexes such as the ribosome. In the present study, the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the ribosome from the microsporidium Vairimorpha necatrix is presented, which illustrates how genome compaction has resulted in the smallest known eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosome. Selection pressure led to the loss of two ribosomal proteins and removal of essentially all eukaryote-specific ribosomal RNA (rRNA) expansion segments, reducing the rRNA to a functionally conserved core. The structure highlights how one microsporidia-specific and several repurposed existing ribosomal proteins compensate for the extensive rRNA reduction. The microsporidian ribosome is kept in an inactive state by two previously uncharacterized dormancy factors that specifically target the functionally important E-site, P-site and polypeptide exit tunnel. The present study illustrates the distinct effects of evolutionary pressure on RNA and protein-coding genes, provides a mechanism for ribosome inhibition and can serve as a structural basis for the development of inhibitors against microsporidian parasites. |
 External links External links |  Nat Microbiol / Nat Microbiol /  PubMed:31332387 / PubMed:31332387 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.26 - 3.7 Å |
| Structure data | 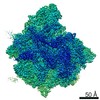 EMDB-4931:  EMDB-4932:  EMDB-4933: 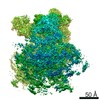 EMDB-4934: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ZN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / Microsporidia / Intracellular Parasite |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



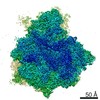
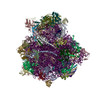
 vairimorpha necatrix (fungus)
vairimorpha necatrix (fungus)