+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Quinone extraction drives atmospheric carbon monoxide oxidation in bacteria. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Chem Biol, Vol. 21, Issue 7, Page 1058-1068, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Jan 29, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Ashleigh Kropp / David L Gillett / Hari Venugopal / Miguel A Gonzálvez / James P Lingford / Surbhi Jain / Christopher K Barlow / Jie Zhang / Chris Greening / Rhys Grinter /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Diverse bacteria and archaea use atmospheric CO as an energy source for long-term survival. Bacteria use [MoCu]-CO dehydrogenases (Mo-CODH) to convert atmospheric CO to carbon dioxide, transferring ...Diverse bacteria and archaea use atmospheric CO as an energy source for long-term survival. Bacteria use [MoCu]-CO dehydrogenases (Mo-CODH) to convert atmospheric CO to carbon dioxide, transferring the obtained electrons to the aerobic respiratory chain. However, it is unknown how these enzymes oxidize CO at low concentrations and interact with the respiratory chain. Here, we use cryo-electron microscopy and structural modeling to show how Mo-CODH (CoxSML) from Mycobacterium smegmatis interacts with its partner, the membrane-bound menaquinone-binding protein CoxG. We provide electrochemical, biochemical and genetic evidence that Mo-CODH transfers CO-derived electrons to the aerobic respiratory chain through CoxG. Lastly, we show that Mo-CODH and CoxG genetically and structurally associate in diverse bacteria and archaea. These findings reveal the basis of the biogeochemically and ecologically important process of atmospheric CO oxidation, while demonstrating that long-range quinone transport is a general mechanism of energy conservation, which convergently evolved on multiple occasions. |
 External links External links |  Nat Chem Biol / Nat Chem Biol /  PubMed:39881213 / PubMed:39881213 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 1.5 - 1.85 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-42164, PDB-8uem:  PDB-8uds: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-HOH: 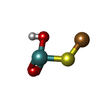 ChemComp-CUN:  ChemComp-MCN: 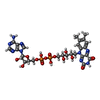 ChemComp-FAD: 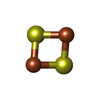 ChemComp-FES: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | ELECTRON TRANSPORT / Menaquinone Binding / Lipid Anchored / Carbon monoxide dehydrogenase / SRPBCC family protein / OXIDOREDUCTASE / MoCu / Mycobacterium smegmatis / High affinity / trace gas scavenging |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 mycolicibacterium smegmatis mc2 155 (bacteria)
mycolicibacterium smegmatis mc2 155 (bacteria)