+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural basis for Na1.7 inhibition by pore blockers. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Struct Mol Biol, Vol. 29, Issue 12, Page 1208-1216, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Nov 24, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Jiangtao Zhang / Yiqiang Shi / Zhuo Huang / Yue Li / Bei Yang / Jianke Gong / Daohua Jiang /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Voltage-gated sodium channel Na1.7 plays essential roles in pain and odor perception. Na1.7 variants cause pain disorders. Accordingly, Na1.7 has elicited extensive attention in developing new ...Voltage-gated sodium channel Na1.7 plays essential roles in pain and odor perception. Na1.7 variants cause pain disorders. Accordingly, Na1.7 has elicited extensive attention in developing new analgesics. Here we present cryo-EM structures of human Na1.7/β1/β2 complexed with inhibitors XEN907, TC-N1752 and Na1.7-IN2, explaining specific binding sites and modulation mechanism for the pore blockers. These inhibitors bind in the central cavity blocking ion permeation, but engage different parts of the cavity wall. XEN907 directly causes α- to π-helix transition of DIV-S6 helix, which tightens the fast inactivation gate. TC-N1752 induces π-helix transition of DII-S6 helix mediated by a conserved asparagine on DIII-S6, which closes the activation gate. Na1.7-IN2 serves as a pore blocker without causing conformational change. Electrophysiological results demonstrate that XEN907 and TC-N1752 stabilize Na1.7 in inactivated state and delay the recovery from inactivation. Our results provide structural framework for Na1.7 modulation by pore blockers, and important implications for developing subtype-selective analgesics. |
 External links External links |  Nat Struct Mol Biol / Nat Struct Mol Biol /  PubMed:36424527 PubMed:36424527 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.07 - 3.22 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-33292: Sodium channel EMDB-33295, PDB-7xmf: EMDB-33296: Sodium channel |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NAG:  ChemComp-G2E: 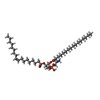 ChemComp-6OU:  ChemComp-G2W: 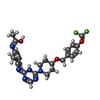 ChemComp-G4I: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / Sodium channel / PROTEIN TRANSPORT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers









 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
