+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
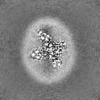
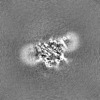
| Title | Sodium channel | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Sodium channel / PROTEIN TRANSPORT | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationresponse to pyrethroid / corticospinal neuron axon guidance / positive regulation of voltage-gated sodium channel activity / action potential propagation / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception / voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane depolarization / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / membrane depolarization during Purkinje myocyte cell action potential / cardiac conduction ...response to pyrethroid / corticospinal neuron axon guidance / positive regulation of voltage-gated sodium channel activity / action potential propagation / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception / voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane depolarization / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / membrane depolarization during Purkinje myocyte cell action potential / cardiac conduction / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane depolarization during action potential / positive regulation of sodium ion transport / regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transport / axon initial segment / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / node of Ranvier / voltage-gated sodium channel complex / sodium channel inhibitor activity / neuronal action potential propagation / locomotion / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / behavioral response to pain / intercalated disc / sodium channel regulator activity / membrane depolarization / neuronal action potential / cardiac muscle contraction / T-tubule / sensory perception of pain / axon terminus / axon guidance / sodium ion transmembrane transport / post-embryonic development / circadian rhythm / positive regulation of neuron projection development / response to toxic substance / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / nervous system development / response to heat / gene expression / chemical synaptic transmission / perikaryon / transmembrane transporter binding / cell adhesion / inflammatory response / axon / synapse / extracellular region / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.09 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jiang DH / Zhang JT | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2022Title: Structural basis for Na1.7 inhibition by pore blockers. Authors: Jiangtao Zhang / Yiqiang Shi / Zhuo Huang / Yue Li / Bei Yang / Jianke Gong / Daohua Jiang /  Abstract: Voltage-gated sodium channel Na1.7 plays essential roles in pain and odor perception. Na1.7 variants cause pain disorders. Accordingly, Na1.7 has elicited extensive attention in developing new ...Voltage-gated sodium channel Na1.7 plays essential roles in pain and odor perception. Na1.7 variants cause pain disorders. Accordingly, Na1.7 has elicited extensive attention in developing new analgesics. Here we present cryo-EM structures of human Na1.7/β1/β2 complexed with inhibitors XEN907, TC-N1752 and Na1.7-IN2, explaining specific binding sites and modulation mechanism for the pore blockers. These inhibitors bind in the central cavity blocking ion permeation, but engage different parts of the cavity wall. XEN907 directly causes α- to π-helix transition of DIV-S6 helix, which tightens the fast inactivation gate. TC-N1752 induces π-helix transition of DII-S6 helix mediated by a conserved asparagine on DIII-S6, which closes the activation gate. Na1.7-IN2 serves as a pore blocker without causing conformational change. Electrophysiological results demonstrate that XEN907 and TC-N1752 stabilize Na1.7 in inactivated state and delay the recovery from inactivation. Our results provide structural framework for Na1.7 modulation by pore blockers, and important implications for developing subtype-selective analgesics. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_33296.map.gz emd_33296.map.gz | 59.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-33296-v30.xml emd-33296-v30.xml emd-33296.xml emd-33296.xml | 22.7 KB 22.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_33296.png emd_33296.png | 49.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-33296.cif.gz emd-33296.cif.gz | 8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_33296_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33296_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33296_half_map_2.map.gz emd_33296_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.3 MB 59.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33296 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33296 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33296 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33296 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7xmgMC  7xm9C  7xmfC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_33296.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_33296.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.04 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
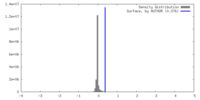
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_33296_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
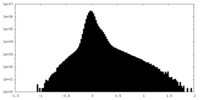
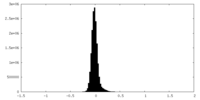
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_33296_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
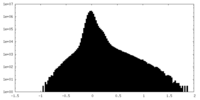
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Sodium channel
| Entire | Name: Sodium channel |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Sodium channel
| Supramolecule | Name: Sodium channel / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Isoform 3 of Sodium channel protein type 9 subunit alpha,Green fl...
| Macromolecule | Name: Isoform 3 of Sodium channel protein type 9 subunit alpha,Green fluorescent protein type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: The fusion protein of Sodium channel, linker, GFP, and tag Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 255.679906 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAMLPPPGPQ SFVHFTKQSL ALIEQRIAER KSKEPKEEKK DDDEEAPKPS SDLEAGKQLP FIYGDIPPGM VSEPLEDLDP YYADKKTFI VLNKGKTIFR FNATPALYML SPFSPLRRIS IKILVHSLFS MLIMCTILTN CIFMTMNNPP DWTKNVEYTF T GIYTFESL ...String: MAMLPPPGPQ SFVHFTKQSL ALIEQRIAER KSKEPKEEKK DDDEEAPKPS SDLEAGKQLP FIYGDIPPGM VSEPLEDLDP YYADKKTFI VLNKGKTIFR FNATPALYML SPFSPLRRIS IKILVHSLFS MLIMCTILTN CIFMTMNNPP DWTKNVEYTF T GIYTFESL VKILARGFCV GEFTFLRDPW NWLDFVVIVF AYLTEFVNLG NVSALRTFRV LRALKTISVI PGLKTIVGAL IQ SVKKLSD VMILTVFCLS VFALIGLQLF MGNLKHKCFR NSLENNETLE SIMNTLESEE DFRKYFYYLE GSKDALLCGF STD SGQCPE GYTCVKIGRN PDYGYTSFDT FSWAFLALFR LMTQDYWENL YQQTLRAAGK TYMIFFVVVI FLGSFYLINL ILAV VAMAY EEQNQANIEE AKQKELEFQQ MLDRLKKEQE EAEAIAAAAA EYTSIRRSRI MGLSESSSET SKLSSKSAKE RRNRR KKKN QKKLSSGEEK GDAEKLSKSE SEDSIRRKSF HLGVEGHRRA HEKRLSTPNQ SPLSIRGSLF SARRSSRTSL FSFKGR GRD IGSETEFADD EHSIFGDNES RRGSLFVPHR PQERRSSNIS QASRSPPMLP VNGKMHSAVD CNGVVSLVDG RSALMLP NG QLLPEGTTNQ IHKKRRCSSY LLSEDMLNDP NLRQRAMSRA SILTNTVEEL EESRQKCPPW WYRFAHKFLI WNCSPYWI K FKKCIYFIVM DPFVDLAITI CIVLNTLFMA MEHHPMTEEF KNVLAIGNLV FTGIFAAEMV LKLIAMDPYE YFQVGWNIF DSLIVTLSLV ELFLADVEGL SVLRSFRLLR VFKLAKSWPT LNMLIKIIGN SVGALGNLTL VLAIIVFIFA VVGMQLFGKS YKECVCKIN DDCTLPRWHM NDFFHSFLIV FRVLCGEWIE TMWDCMEVAG QAMCLIVYMM VMVIGNLVVL NLFLALLLSS F SSDNLTAI EEDPDANNLQ IAVTRIKKGI NYVKQTLREF ILKAFSKKPK ISREIRQAED LNTKKENYIS NHTLAEMSKG HN FLKEKDK ISGFGSSVDK HLMEDSDGQS FIHNPSLTVT VPIAPGESDL ENMNAEELSS DSDSEYSKVR LNRSSSSECS TVD NPLPGE GEEAEAEPMN SDEPEACFTD GCVRRFSCCQ VNIESGKGKI WWNIRKTCYK IVEHSWFESF IVLMILLSSG ALAF EDIYI ERKKTIKIIL EYADKIFTYI FILEMLLKWI AYGYKTYFTN AWCWLDFLIV DVSLVTLVAN TLGYSDLGPI KSLRT LRAL RPLRALSRFE GMRVVVNALI GAIPSIMNVL LVCLIFWLIF SIMGVNLFAG KFYECINTTD GSRFPASQVP NRSECF ALM NVSQNVRWKN LKVNFDNVGL GYLSLLQVAT FKGWTIIMYA AVDSVNVDKQ PKYEYSLYMY IYFVVFIIFG SFFTLNL FI GVIIDNFNQQ KKKLGGQDIF MTEEQKKYYN AMKKLGSKKP QKPIPRPGNK IQGCIFDLVT NQAFDISIMV LICLNMVT M MVEKEGQSQH MTEVLYWINV VFIILFTGEC VLKLISLRHY YFTVGWNIFD FVVVIISIVG MFLADLIETY FVSPTLFRV IRLARIGRIL RLVKGAKGIR TLLFALMMSL PALFNIGLLL FLVMFIYAIF GMSNFAYVKK EDGINDMFNF ETFGNSMICL FQITTSAGW DGLLAPILNS KPPDCDPKKV HPGSSVEGDC GNPSVGIFYF VSYIIISFLV VVNMYIAVIL ENFSVATEES T EPLSEDDF EMFYEVWEKF DPDATQFIEF SKLSDFAAAL DPPLLIAKPN KVQLIAMDLP MVSGDRIHCL DILFAFTKRV LG ESGEMDS LRSQMEERFM SANPSKVSYE PITTTLKRKQ EDVSATVIQR AYRRYRLRQN VKNISSIYIK DGDRDDDLLN KKD MAFDNV NENSSPEKTD ATSSTTSPPS YDSVTKPDKE KYEQDRTEKE DKGKDSKESK KAAALEVLFQ GPSKGEELFT GVVP ILVEL DGDVNGHKFS VRGEGEGDAT NGKLTLKFIC TTGKLPVPWP TLVTTLTYGV QCFSRYPDHM KRHDFFKSAM PEGYV QERT ISFKDDGTYK TRAEVKFEGD TLVNRIELKG IDFKEDGNIL GHKLEYNFNS HNVYITADKQ KNGIKANFKI RHNVED GSV QLADHYQQNT PIGDGPVLLP DNHYLSTQSV LSKDPNEKRD HMVLLEFVTA AGITHGMDEW SHPQFEKGGG SGGGSGG SA WSHPQFEK UniProtKB: Sodium channel protein type 9 subunit alpha |
-Macromolecule #2: Sodium channel subunit beta-1,Green fluorescent protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Sodium channel subunit beta-1,Green fluorescent protein type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 Details: The fusion protein of Sodium channel, linker, GFP, and tag Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 54.472129 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGRLLALVVG AALVSSACGG CVEVDSETEA VYGMTFKILC ISCKRRSETN AETFTEWTFR QKGTEEFVKI LRYENEVLQL EEDERFEGR VVWNGSRGTK DLQDLSIFIT NVTYNHSGDY ECHVYRLLFF ENYEHNTSVV KKIHIEVVDK ANRDMASIVS E IMMYVLIV ...String: MGRLLALVVG AALVSSACGG CVEVDSETEA VYGMTFKILC ISCKRRSETN AETFTEWTFR QKGTEEFVKI LRYENEVLQL EEDERFEGR VVWNGSRGTK DLQDLSIFIT NVTYNHSGDY ECHVYRLLFF ENYEHNTSVV KKIHIEVVDK ANRDMASIVS E IMMYVLIV VLTIWLVAEM IYCYKKIAAA TETAAQENAS EYLAITSESK ENCTGVQVAE AAALEVLFQG PSKGEELFTG VV PILVELD GDVNGHKFSV RGEGEGDATN GKLTLKFICT TGKLPVPWPT LVTTLTYGVQ CFSRYPDHMK RHDFFKSAMP EGY VQERTI SFKDDGTYKT RAEVKFEGDT LVNRIELKGI DFKEDGNILG HKLEYNFNSH NVYITADKQK NGIKANFKIR HNVE DGSVQ LADHYQQNTP IGDGPVLLPD NHYLSTQSVL SKDPNEKRDH MVLLEFVTAA GITHGMDEHH HHHHHHHHDY KDDDD K UniProtKB: Sodium channel regulatory subunit beta-1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Sodium channel subunit beta-2
| Macromolecule | Name: Sodium channel subunit beta-2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.355859 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MHRDAWLPRP AFSLTGLSLF FSLVPPGRSM EVTVPATLNV LNGSDARLPC TFNSCYTVNH KQFSLNWTYQ ECNNCSEEMF LQFRMKIIN LKLERFQDRV EFSGNPSKYD VSVMLRNVQP EDEGIYNCYI MNPPDRHRGH GKIHLQVLME EPPERDSTVA V IVGASVGG ...String: MHRDAWLPRP AFSLTGLSLF FSLVPPGRSM EVTVPATLNV LNGSDARLPC TFNSCYTVNH KQFSLNWTYQ ECNNCSEEMF LQFRMKIIN LKLERFQDRV EFSGNPSKYD VSVMLRNVQP EDEGIYNCYI MNPPDRHRGH GKIHLQVLME EPPERDSTVA V IVGASVGG FLAVVILVLM VVKCVRRKKE QKLSTDDLKT EEEGKTDGEG NPDDGAK UniProtKB: Sodium channel regulatory subunit beta-2 |
-Macromolecule #5: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #6: (1~{Z})-~{N}-[2-methyl-3-[(~{E})-[6-[4-[[4-(trifluoromethyloxy)ph...
| Macromolecule | Name: (1~{Z})-~{N}-[2-methyl-3-[(~{E})-[6-[4-[[4-(trifluoromethyloxy)phenyl]methoxy]piperidin-1-yl]-1~{H}-1,3,5-triazin-2-ylidene]amino]phenyl]ethanimidic acid type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: G4I |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 516.515 Da |
| Chemical component information | 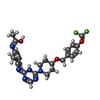 ChemComp-G4I: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)