+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Dimeric Organization of Blood Coagulation Factor VIII bound to Lipid Nanotubes. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Sci Rep, Vol. 5, Page 11212, Year 2015 |
| Publish date | Jun 17, 2015 |
 Authors Authors | Daniela Dalm / Jesus G Galaz-Montoya / Jaimy L Miller / Kirill Grushin / Alex Villalobos / Alexey Y Koyfman / Michael F Schmid / Svetla Stoilova-McPhie /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Membrane-bound Factor VIII (FVIII) has a critical function in blood coagulation as the pro-cofactor to the serine-protease Factor IXa (FIXa) in the FVIIIa-FIXa complex assembled on the activated ...Membrane-bound Factor VIII (FVIII) has a critical function in blood coagulation as the pro-cofactor to the serine-protease Factor IXa (FIXa) in the FVIIIa-FIXa complex assembled on the activated platelet membrane. Defects or deficiency of FVIII cause Hemophilia A, a mild to severe bleeding disorder. Despite existing crystal structures for FVIII, its membrane-bound organization has not been resolved. Here we present the dimeric FVIII membrane-bound structure when bound to lipid nanotubes, as determined by cryo-electron microscopy. By combining the structural information obtained from helical reconstruction and single particle subtomogram averaging at intermediate resolution (15-20 Å), we show unambiguously that FVIII forms dimers on lipid nanotubes. We also demonstrate that the organization of the FVIII membrane-bound domains is consistently different from the crystal structure in solution. The presented results are a critical step towards understanding the mechanism of the FVIIIa-FIXa complex assembly on the activated platelet surface in the propagation phase of blood coagulation. |
 External links External links |  Sci Rep / Sci Rep /  PubMed:26082135 / PubMed:26082135 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (subtomogram averaging) / EM (helical sym.) |
| Resolution | 15.5 - 21.0 Å |
| Structure data | 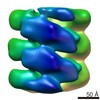 EMDB-3026:  EMDB-3027: |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




