+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | A trimeric human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as an anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Struct Mol Biol, Vol. 28, Issue 2, Page 202-209, Year 2021 |
| Publish date | Jan 11, 2021 |
 Authors Authors | Tianshu Xiao / Jianming Lu / Jun Zhang / Rebecca I Johnson / Lindsay G A McKay / Nadia Storm / Christy L Lavine / Hanqin Peng / Yongfei Cai / Sophia Rits-Volloch / Shen Lu / Brian D Quinlan / Michael Farzan / Michael S Seaman / Anthony Griffiths / Bing Chen /  |
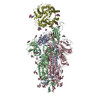
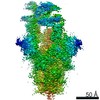
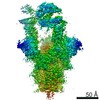
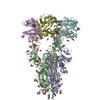
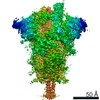
| PubMed Abstract | Effective intervention strategies are urgently needed to control the COVID-19 pandemic. Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a membrane-bound carboxypeptidase that forms a dimer and serves ...Effective intervention strategies are urgently needed to control the COVID-19 pandemic. Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a membrane-bound carboxypeptidase that forms a dimer and serves as the cellular receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). ACE2 is also a key negative regulator of the renin-angiotensin system that modulates vascular functions. We report here the properties of a trimeric ACE2 ectodomain variant, engineered using a structure-based approach. The trimeric ACE2 variant has a binding affinity of ~60 pM for the spike protein of SARS‑CoV‑2 (compared with 77 nM for monomeric ACE2 and 12-22 nM for dimeric ACE2 constructs), and its peptidase activity and the ability to block activation of angiotensin II receptor type 1 in the renin-angiotensin system are preserved. Moreover, the engineered ACE2 potently inhibits SARS‑CoV‑2 infection in cell culture. These results suggest that engineered, trimeric ACE2 may be a promising anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent for treating COVID-19. |
 External links External links |  Nat Struct Mol Biol / Nat Struct Mol Biol /  PubMed:33432247 / PubMed:33432247 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.4 - 3.7 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-22891, PDB-7kj2: EMDB-22892, PDB-7kj3: EMDB-22893, PDB-7kj4: EMDB-22894, PDB-7kj5: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NAG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN/HYDROLASE / VIRAL PROTEIN / VIRAL PROTEIN-HYDROLASE complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers






 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)