+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Crystal structure of the flavin reductase of Acinetobacter baumannii p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase (HPAH) and identification of amino acid residues underlying its regulation by aromatic ligands. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Arch Biochem Biophys, Vol. 653, Page 24-38, Year 2018 |
| Publish date | Sep 1, 2018 |
 Authors Authors | Anan Yuenyao / Nopphon Petchyam / Nuntaporn Kamonsutthipaijit / Pimchai Chaiyen / Danaya Pakotiprapha /  |
| PubMed Abstract | The first step in the degradation of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) is catalyzed by the two-component enzyme p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase (HPAH). The two components of Acinetobacter ...The first step in the degradation of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) is catalyzed by the two-component enzyme p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase (HPAH). The two components of Acinetobacter baumannii HPAH are known as C and C, respectively. C is a flavin reductase that uses NADH to generate reduced flavin mononucleotide (FMNH), which is used by C in the hydroxylation of HPA. Interestingly, although HPA is not directly involved in the reaction catalyzed by C, the presence of HPA dramatically increases the FMN reduction rate. Amino acid sequence analysis revealed that C contains two domains: an N-terminal flavin reductase domain, and a C-terminal MarR domain. Although MarR proteins typically function as transcription regulators, the MarR domain of C was found to play an auto-inhibitory role. Here, we report a crystal structure of C and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) studies that revealed that C undergoes a substantial conformational change in the presence of HPA, concomitant with the increase in the rate of flavin reduction. Amino acid residues that are important for HPA binding and regulation of C activity were identified by site-directed mutagenesis. Amino acid sequence similarity analysis revealed several as yet uncharacterized flavin reductases with N- or C-terminal fusions. |
 External links External links |  Arch Biochem Biophys / Arch Biochem Biophys /  PubMed:29940152 PubMed:29940152 |
| Methods | SAS (X-ray synchrotron) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.898 Å |
| Structure data |  SASDD24: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of H170A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 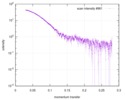 SASDD28: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of E251A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDD34: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of H170A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDD38: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of E251A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDD44: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of H170A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 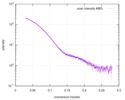 SASDD48: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of E251A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 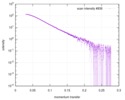 SASDD54: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of H170A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 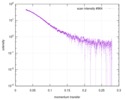 SASDD58: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of E251A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDD64: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of H170A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDD68: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of E251A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDD74: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of S172A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 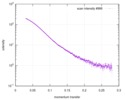 SASDD78: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of E251A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 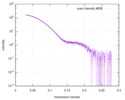 SASDD84: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of S172A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDD94: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of S172A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDA4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of S172A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 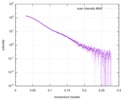 SASDDB4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of S172A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDC4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of S172A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDD4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of N174A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDE4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of N174A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDF4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of N174A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDG4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of N174A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 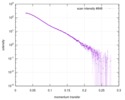 SASDDH4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of N174A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDJ4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of Y207A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 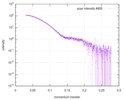 SASDDK4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of Y207A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 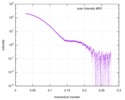 SASDDL4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of Y207A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 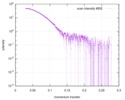 SASDDM4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of Y207A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDN4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of Y207A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 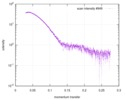 SASDDN7: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of E248A/E251A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 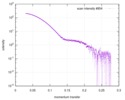 SASDDP4: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of Y207A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDP7: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of E248A/E251A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 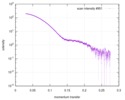 SASDDQ7: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of E248A/E251A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 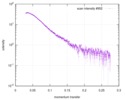 SASDDR7: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of E248A/E251A C1 in the presence of 1 mM p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDS7: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of E248A/E251A C1 in the presence of 1 mM p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 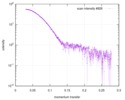 SASDDT3: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component: 2 mg/ml of wild-type C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 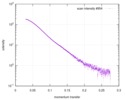 SASDDT7: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of E248A/E251A C1 in the presence of 1 mM p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDU3: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component: 4 mg/ml of Wild-type C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDU7: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of E248A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 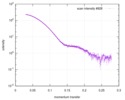 SASDDV3: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component: 8 mg/ml of Wild-type C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 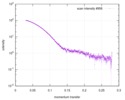 SASDDV7: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of E248A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 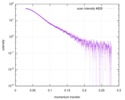 SASDDW3: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component: 2 mg/ml of Wild-type C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 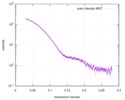 SASDDW7: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of E248A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 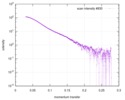 SASDDX3: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component: 4 mg/ml of Wild-type C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDX7: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of E248A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 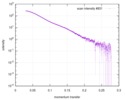 SASDDY3: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component: 8 mg/ml of Wild-type C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDY7: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 4 mg/ml of E248A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) 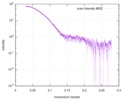 SASDDZ3: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 2 mg/ml of H170A C1 in the absence of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  SASDDZ7: p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, reductase component (mutant): 8 mg/ml of E248A C1 in 1 mM of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA)  PDB-5zc2: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-FMN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  FLAVOPROTEIN / FLAVOPROTEIN /  Flavin reductase / MarR Flavin reductase / MarR |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




