+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Combined roles of ATP and small hairpin RNA in the activation of RIG-I revealed by solution-based analysis. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nucleic Acids Res, Vol. 46, Issue 6, Page 3169-3186, Year 2018 |
| 掲載日 | 2018年4月6日 |
 著者 著者 | Neelam Shah / Simone A Beckham / Jacqueline A Wilce / Matthew C J Wilce /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | RIG-I (retinoic acid inducible gene-I) is a cytosolic innate immune protein that senses viral dsRNA with a 5'-triphosphate overhang. Upon interaction with dsRNA a de-repression of the RIG-I CARD ...RIG-I (retinoic acid inducible gene-I) is a cytosolic innate immune protein that senses viral dsRNA with a 5'-triphosphate overhang. Upon interaction with dsRNA a de-repression of the RIG-I CARD domains takes place that ultimately leads to the production of type I interferons and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Here we investigate the RIG-I conformational rearrangement upon interaction with an activating 5'-triphosphate-10-base pair dsRNA hairpin loop (10bp) compared with a less active 5'-triphosphate-8-base pair dsRNA hairpin loop (8bp). We use size-exclusion chromatography-coupled small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and limited tryptic digest experiments to show that that upon binding to 10 bp, but not 8 bp, RIG-I becomes extended and shows greater flexibility, reflecting the release of its CARDs. We also examined the effect of different ATP analogues on the conformational changes of RIG-I/dsRNA complexes. Of the analogues tested, the addition of ATP transition state analogue ADP-AlFx further assisted in the complete activation of RIG-I in complex with 10bp and also to some extent RIG-I bound to 8bp. Together these data provide solution-based evidence for the molecular mechanism of innate immune signaling by RIG-I as stimulated by short hairpin RNA and ATP. |
 リンク リンク |  Nucleic Acids Res / Nucleic Acids Res /  PubMed:29346611 / PubMed:29346611 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | SAS (X-ray synchrotron) |
| 構造データ | 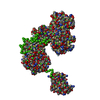 SASDB78: 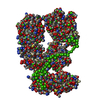 SASDB88:  SASDB98: 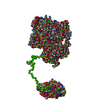 SASDBA8:  SASDBB8: 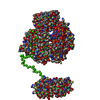 SASDBD8:  SASDBE8:  SASDBF8:  SASDBG8:  SASDBH8:  SASDBJ8:  SASDBK8:  SASDBL8:  SASDBM8:  SASDBN8:  SASDBP8:  SASDBQ8: Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX58 (Full-length RIG-I) plus 8mer hairpin dsRNA (SEC-peak2)  SASDBR8: Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX58 (Full-length RIG-I), 8mer hairpin dsRNA/AMP-PNP (SECpeak2)  SASDBS8: Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX58 (Full-length RIG-I) 8mer hairpin dsRNA/ADP-AlFx (SECpeak2) 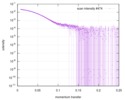 SASDBT8: Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX58 (Delta-CARDs RIG-I) plus 8mer hairpin dsRNA (SEC-peak2) 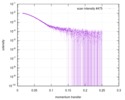 SASDBU8: Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX58 (Delta-CARDs) plus 8mer hairpin dsRNA/AMP-PNP (SEC-peak2)  SASDBV8: |
| 由来 |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について



 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)