+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Cytoskeletal regulation of a transcription factor by DNA mimicry via coiled-coil interactions. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nat Cell Biol, Vol. 24, Issue 7, Page 1088-1098, Year 2022 |
| 掲載日 | 2022年6月20日 |
 著者 著者 | Farah Haque / Christian Freniere / Qiong Ye / Nandini Mani / Elizabeth M Wilson-Kubalek / Pei-I Ku / Ronald A Milligan / Radhika Subramanian /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | A long-established strategy for transcription regulation is the tethering of transcription factors to cellular membranes. By contrast, the principal effectors of Hedgehog signalling, the GLI ...A long-established strategy for transcription regulation is the tethering of transcription factors to cellular membranes. By contrast, the principal effectors of Hedgehog signalling, the GLI transcription factors, are regulated by microtubules in the primary cilium and the cytoplasm. How GLI is tethered to microtubules remains unclear. Here, we uncover DNA mimicry by the ciliary kinesin KIF7 as a mechanism for the recruitment of GLI to microtubules, wherein the coiled-coil dimerization domain of KIF7, characterized by its striking shape, size and charge similarity to DNA, forms a complex with the DNA-binding zinc fingers in GLI, thus revealing a mode of tethering a DNA-binding protein to the cytoskeleton. GLI increases KIF7 microtubule affinity and consequently modulates the localization of both proteins to microtubules and the cilium tip. Thus, the kinesin-microtubule system is not a passive GLI tether but a regulatable platform tuned by the kinesin-transcription factor interaction. We retooled this coiled-coil-based GLI-KIF7 interaction to inhibit the nuclear and cilium localization of GLI. This strategy can potentially be exploited to downregulate erroneously activated GLI in human cancers. |
 リンク リンク |  Nat Cell Biol / Nat Cell Biol /  PubMed:35725768 / PubMed:35725768 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (らせん対称) |
| 解像度 | 3.89 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-24721, PDB-7rx0: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-ANP:  ChemComp-GTP: 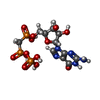 ChemComp-G2P:  ChemComp-MG: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | MOTOR PROTEIN / Kinesin / Microtubule / Transcription factor / motor domain |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について



 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト)
