+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Cryo-EM structure of native human uromodulin, a zona pellucida module polymer. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | EMBO J, Vol. 39, Issue 24, Page e106807, Year 2020 |
| 掲載日 | 2020年12月15日 |
 著者 著者 | Alena Stsiapanava / Chenrui Xu / Martina Brunati / Sara Zamora-Caballero / Céline Schaeffer / Marcel Bokhove / Ling Han / Hans Hebert / Marta Carroni / Shigeki Yasumasu / Luca Rampoldi / Bin Wu / Luca Jovine /     |
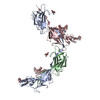
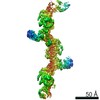
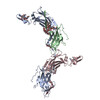
| PubMed 要旨 | Assembly of extracellular filaments and matrices mediating fundamental biological processes such as morphogenesis, hearing, fertilization, and antibacterial defense is driven by a ubiquitous ...Assembly of extracellular filaments and matrices mediating fundamental biological processes such as morphogenesis, hearing, fertilization, and antibacterial defense is driven by a ubiquitous polymerization module known as zona pellucida (ZP) "domain". Despite the conservation of this element from hydra to humans, no detailed information is available on the filamentous conformation of any ZP module protein. Here, we report a cryo-electron microscopy study of uromodulin (UMOD)/Tamm-Horsfall protein, the most abundant protein in human urine and an archetypal ZP module-containing molecule, in its mature homopolymeric state. UMOD forms a one-start helix with an unprecedented 180-degree twist between subunits enfolded by interdomain linkers that have completely reorganized as a result of propeptide dissociation. Lateral interaction between filaments in the urine generates sheets exposing a checkerboard of binding sites to capture uropathogenic bacteria, and UMOD-based models of heteromeric vertebrate egg coat filaments identify a common sperm-binding region at the interface between subunits. |
 リンク リンク |  EMBO J / EMBO J /  PubMed:33196145 / PubMed:33196145 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (らせん対称) |
| 解像度 | 3.35 - 3.96 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-10553: Cryo-EM of native human uromodulin (UMOD)/Tamm-Horsfall protein (THP) filament EMDB-10554, PDB-6tql: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-NAG: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / ZP MODULE / ZP DOMAIN / ZP-N DOMAIN / ZP-C DOMAIN / INTERDOMAIN LINKER / EGF DOMAIN / EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX / GLYCOPROTEIN / N-GLYCAN / PROTEIN FILAMENT / PROTEIN POLYMERIZATION |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について




 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト)