+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Bile Salts Alter the Mouse Norovirus Capsid Conformation: Possible Implications for Cell Attachment and Immune Evasion. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | J Virol, Vol. 93, Issue 19, Year 2019 |
| 掲載日 | 2019年10月1日 |
 著者 著者 | Michael B Sherman / Alexis N Williams / Hong Q Smith / Christopher Nelson / Craig B Wilen / Daved H Fremont / Herbert W Virgin / Thomas J Smith /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | Caliciviruses are single-stranded RNA viruses with 180 copies of capsid protein comprising the T=3 icosahedral capsids. The main capsid feature is a pronounced protruding (P) domain dimer formed by ...Caliciviruses are single-stranded RNA viruses with 180 copies of capsid protein comprising the T=3 icosahedral capsids. The main capsid feature is a pronounced protruding (P) domain dimer formed by adjacent subunits on the icosahedral surface while the shell domain forms a tight icosahedral sphere around the genome. While the P domain in the crystal structure of human Norwalk virus (genotype I.1) was tightly associated with the shell surface, the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of several members of the family (mouse norovirus [MNV], rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus, and human norovirus genotype II.10) revealed a "floating" P domain that hovers above the shell by nearly 10 to 15 Å in physiological buffers. Since this unusual feature is shared among, and unique to, the , it suggests an important biological role. Recently, we demonstrated that bile salts enhance cell attachment to the target cell and increase the intrinsic affinity between the P domain and receptor. Presented here are the cryo-EM structures of MNV-1 in the presence of bile salts (∼3 Å) and the receptor CD300lf (∼8 Å). Surprisingly, bile salts cause the rotation and contraction of the P domain onto the shell surface. This both stabilizes the P domain and appears to allow for a higher degree of saturation of receptor onto the virus. Together, these results suggest that, as the virus moves into the gut and the associated high concentrations of bile, the entire capsid face undergoes a conformational change to optimize receptor avidity while the P domain itself undergoes smaller conformational changes to improve receptor affinity. Mouse norovirus and several other members of the have been shown to have a highly unusual structure with the receptor binding protruding (P) domain only loosely tethered to the main capsid shell. Recent studies demonstrated that bile salts enhance the intrinsic P domain/receptor affinity and is necessary for cell attachment. Presented here are the high-resolution cryo-EM structures of apo MNV, MNV/bile salt, and MNV/bile salt/receptor. Bile salts cause a 90° rotation and collapse of the P domain onto the shell surface that may increase the number of available receptor binding sites. Therefore, bile salts appear to be having several effects on MNV. Bile salts shift the structural equilibrium of the P domain toward a form that binds the receptor and away from one that binds antibody. They may also cause the entire P domain to optimize receptor binding while burying a number of potential epitopes. |
 リンク リンク |  J Virol / J Virol /  PubMed:31341042 / PubMed:31341042 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.1 - 9.5 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-20250, PDB-6p4j: EMDB-20251, PDB-6p4k: EMDB-20252, PDB-6p4l: 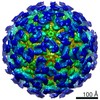 EMDB-20253: |
| 化合物 | 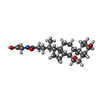 ChemComp-CHO:  ChemComp-TCH: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | VIRUS / norovirus / bile salts / murine / VIRAL PROTEIN |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について



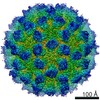






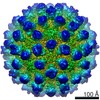 murine norovirus 1 (マウスノロウイルス 1)
murine norovirus 1 (マウスノロウイルス 1)