+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structural basis of Q-dependent antitermination. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 116, Issue 37, Page 18384-18390, Year 2019 |
| 掲載日 | 2019年9月10日 |
 著者 著者 | Zhou Yin / Jason T Kaelber / Richard H Ebright /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | Lambdoid bacteriophage Q protein mediates the switch from middle to late bacteriophage gene expression by enabling RNA polymerase (RNAP) to read through transcription terminators preceding ...Lambdoid bacteriophage Q protein mediates the switch from middle to late bacteriophage gene expression by enabling RNA polymerase (RNAP) to read through transcription terminators preceding bacteriophage late genes. Q loads onto RNAP engaged in promoter-proximal pausing at a Q binding element (QBE) and adjacent sigma-dependent pause element (SDPE) to yield a Q-loading complex, and Q subsequently translocates with RNAP as a pausing-deficient, termination-deficient Q-loaded complex. Here, we report high-resolution structures of 4 states on the pathway of antitermination by Q from bacteriophage 21 (Q21): Q21, the Q21-QBE complex, the Q21-loading complex, and the Q21-loaded complex. The results show that Q21 forms a torus, a "nozzle," that narrows and extends the RNAP RNA-exit channel, extruding topologically linked single-stranded RNA and preventing the formation of pause and terminator hairpins. |
 リンク リンク |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:31455742 / PubMed:31455742 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) / X線回折 |
| 解像度 | 1.942 - 3.8 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-20233, PDB-6p18: EMDB-20234, PDB-6p19: 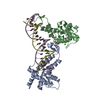 PDB-6p1a:  PDB-6p1b: 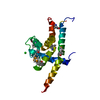 PDB-6p1c: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-ZN:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-EDO:  ChemComp-CL:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | GENE REGULATION / RNA polymerase / DNA Binding / transcription / Q-dependent antitermination / Q antiterminator factor / Q antitermination factor |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について



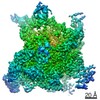
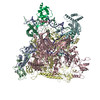


 phage 21 (ファージ)
phage 21 (ファージ)