+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structural Basis of the Proton Sensitivity of Human GluN1-GluN2A NMDA Receptors. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Cell Rep, Vol. 25, Issue 13, Page 3582-33590.e4, Year 2018 |
| 掲載日 | 2018年12月26日 |
 著者 著者 | Jin-Bao Zhang / Shenghai Chang / Pan Xu / Miao Miao / Hangjun Wu / Youyi Zhang / Tongtong Zhang / Han Wang / Jilin Zhang / Chun Xie / Nan Song / Cheng Luo / Xing Zhang / Shujia Zhu /  |
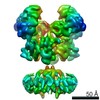
| PubMed 要旨 | N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are critical for synaptic development and plasticity. While glutamate is the primary agonist, protons can modulate NMDA receptor activity at synapses during ...N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are critical for synaptic development and plasticity. While glutamate is the primary agonist, protons can modulate NMDA receptor activity at synapses during vesicle exocytosis by mechanisms that are unknown. We used cryo-electron microscopy to solve the structures of the human GluN1-GluN2A NMDA receptor at pH 7.8 and pH 6.3. Our structures demonstrate that the proton sensor predominantly resides in the N-terminal domain (NTD) of the GluN2A subunit and reveal the allosteric coupling mechanism between the proton sensor and the channel gate. Under high-pH conditions, the GluN2A-NTD adopts an "open-and-twisted" conformation. However, upon protonation at the lower pH, the GluN2A-NTD transits from an open- to closed-cleft conformation, causing rearrangements between the tetrameric NTDs and agonist-binding domains. The conformational mobility observed in our structures (presumably from protonation) is supported by molecular dynamics simulation. Our findings reveal the structural mechanisms by which protons allosterically inhibit human GluN1-GluN2A receptor activity. |
 リンク リンク |  Cell Rep / Cell Rep /  PubMed:30590034 PubMed:30590034 |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 4.5 - 7.8 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-9714, PDB-6ira: EMDB-9715, PDB-6irf: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ionotropic glutamate receptors / NMDA receptors / synaptic protein |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について



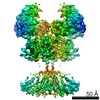
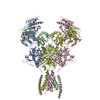
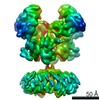

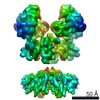


 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト)