+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structure of mammalian endolysosomal TRPML1 channel in nanodiscs. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nature, Vol. 550, Issue 7676, Page 415-418, Year 2017 |
| 掲載日 | 2017年10月19日 |
 著者 著者 | Qingfeng Chen / Ji She / Weizhong Zeng / Jiangtao Guo / Haoxing Xu / Xiao-Chen Bai / Youxing Jiang /  |
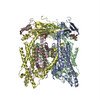
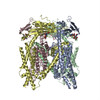
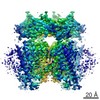
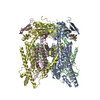
| PubMed 要旨 | Transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1) is a cation channel located within endosomal and lysosomal membranes. Ubiquitously expressed in mammalian cells, its loss-of-function mutations are ...Transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1) is a cation channel located within endosomal and lysosomal membranes. Ubiquitously expressed in mammalian cells, its loss-of-function mutations are the direct cause of type IV mucolipidosis, an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease. Here we present the single-particle electron cryo-microscopy structure of the mouse TRPML1 channel embedded in nanodiscs. Combined with mutagenesis analysis, the TRPML1 structure reveals that phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(3,5)P) binds to the N terminus of the channel-distal from the pore-and the helix-turn-helix extension between segments S2 and S3 probably couples ligand binding to pore opening. The tightly packed selectivity filter contains multiple ion-binding sites, and the conserved acidic residues form the luminal Ca-blocking site that confers luminal pH and Ca modulation on channel conductance. A luminal linker domain forms a fenestrated canopy atop the channel, providing several luminal ion passages to the pore and creating a negative electrostatic trap, with a preference for divalent cations, at the luminal entrance. The structure also reveals two equally distributed S4-S5 linker conformations in the closed channel, suggesting an S4-S5 linker-mediated PtdInsP gating mechanism among TRPML channels. |
 リンク リンク |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:29019981 / PubMed:29019981 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.59 - 3.75 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-8881, PDB-5wpq: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-NA: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Ion channel |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について