+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structure of an Ancient Respiratory System. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Cell, Vol. 173, Issue 7, Page 1636-1649.e16, Year 2018 |
| 掲載日 | 2018年6月14日 |
 著者 著者 | Hongjun Yu / Chang-Hao Wu / Gerrit J Schut / Dominik K Haja / Gongpu Zhao / John W Peters / Michael W W Adams / Huilin Li /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | Hydrogen gas-evolving membrane-bound hydrogenase (MBH) and quinone-reducing complex I are homologous respiratory complexes with a common ancestor, but a structural basis for their evolutionary ...Hydrogen gas-evolving membrane-bound hydrogenase (MBH) and quinone-reducing complex I are homologous respiratory complexes with a common ancestor, but a structural basis for their evolutionary relationship is lacking. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of a 14-subunit MBH from the hyperthermophile Pyrococcus furiosus. MBH contains a membrane-anchored hydrogenase module that is highly similar structurally to the quinone-binding Q-module of complex I while its membrane-embedded ion-translocation module can be divided into a H- and a Na-translocating unit. The H-translocating unit is rotated 180° in-membrane with respect to its counterpart in complex I, leading to distinctive architectures for the two respiratory systems despite their largely conserved proton-pumping mechanisms. The Na-translocating unit, absent in complex I, resembles that found in the Mrp H/Na antiporter and enables hydrogen gas evolution by MBH to establish a Na gradient for ATP synthesis near 100°C. MBH also provides insights into Mrp structure and evolution of MBH-based respiratory enzymes. |
 リンク リンク |  Cell / Cell /  PubMed:29754813 / PubMed:29754813 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.7 Å |
| 構造データ | |
| 化合物 | 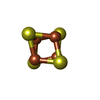 ChemComp-SF4: 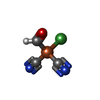 ChemComp-NFU: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / respiratory / hydrogenase / ion translocation |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について






 Pyrococcus furiosus (古細菌)
Pyrococcus furiosus (古細菌)