+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structural and biochemical mechanism of short-chain enoyl-CoA hydratase (ECHS1) substrate recognition. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Commun Biol, Vol. 8, Issue 1, Page 619, Year 2025 |
| 掲載日 | 2025年4月16日 |
 著者 著者 | Gengchen Su / Youwei Xu / Binxian Chen / Kaide Ju / Ye Jin / Houzao Chen / Shuyang Zhang / Xiaodong Luan /  |
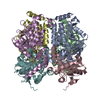
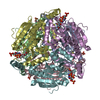
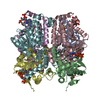
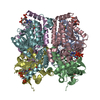
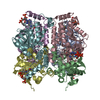
| PubMed 要旨 | Deficiency of short-chain enoyl-CoA hydratase (ECHS1), a crucial enzyme in fatty acid metabolism through the mitochondrial β-oxidation pathway, has been strongly linked to various diseases, ...Deficiency of short-chain enoyl-CoA hydratase (ECHS1), a crucial enzyme in fatty acid metabolism through the mitochondrial β-oxidation pathway, has been strongly linked to various diseases, especially cardiomyopathy. However, the structural and biochemical mechanisms through which ECHS1 recognizes acyl-CoAs remain poorly understood. Herein, cryo-EM analysis reveals the apo structure of ECHS1 and structures of the ECHS1-crotonyl-CoA, ECHS1-acetoacetyl-CoA, ECHS1-hexanoyl-CoA, and ECHS1-octanoyl-CoA complexes at high resolutions. The mechanism through which ECHS1 recognizes its substrates varies with the fatty acid chain lengths of acyl-CoAs. Furthermore, crucial point mutations in ECHS1 have a great impact on substrate recognition, resulting in significant changes in binding affinity and enzyme activity, as do disease-related point mutations in ECHS1. The functional mechanism of ECHS1 is systematically elucidated from structural and biochemical perspectives. These findings provide a theoretical basis for subsequent work focused on determining the role of ECHS1 deficiency (ECHS1D) in the occurrence of diseases such as cardiomyopathy. |
 リンク リンク |  Commun Biol / Commun Biol /  PubMed:40240482 / PubMed:40240482 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 2.18 - 2.55 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-60405, PDB-8zru: EMDB-60406, PDB-8zrv: EMDB-60407, PDB-8zrw: EMDB-60408, PDB-8zrx: EMDB-60409, PDB-8zry: |
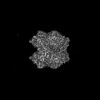
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-HXC: 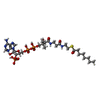 ChemComp-CO8:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-CAA:  PDB-1d88: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | HYDROLASE / ECHS1 / Hexanoyl-CoA / Octanoyl-CoA / Acetoacetyl-CoA / Crotonoyl-CoA |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について







 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト)