+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Lis1 regulates dynein by sterically blocking its mechanochemical cycle. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Elife, Vol. 3, Year 2014 |
| 掲載日 | 2014年11月7日 |
 著者 著者 | Katerina Toropova / Sirui Zou / Anthony J Roberts / William B Redwine / Brian S Goodman / Samara L Reck-Peterson / Andres E Leschziner /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | Regulation of cytoplasmic dynein's motor activity is essential for diverse eukaryotic functions, including cell division, intracellular transport, and brain development. The dynein regulator Lis1 is ...Regulation of cytoplasmic dynein's motor activity is essential for diverse eukaryotic functions, including cell division, intracellular transport, and brain development. The dynein regulator Lis1 is known to keep dynein bound to microtubules; however, how this is accomplished mechanistically remains unknown. We have used three-dimensional electron microscopy, single-molecule imaging, biochemistry, and in vivo assays to help establish this mechanism. The three-dimensional structure of the dynein-Lis1 complex shows that binding of Lis1 to dynein's AAA+ ring sterically prevents dynein's main mechanical element, the 'linker', from completing its normal conformational cycle. Single-molecule experiments show that eliminating this block by shortening the linker to a point where it can physically bypass Lis1 renders single dynein motors insensitive to regulation by Lis1. Our data reveal that Lis1 keeps dynein in a persistent microtubule-bound state by directly blocking the progression of its mechanochemical cycle. |
 リンク リンク |  Elife / Elife /  PubMed:25380312 / PubMed:25380312 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 14.8 - 23.1 Å |
| 構造データ | 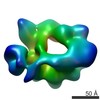 EMDB-6008: 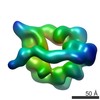 EMDB-6013:  EMDB-6014: 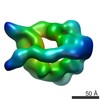 EMDB-6015: 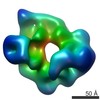 EMDB-6016:  EMDB-6017: |
| 由来 |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について




