+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Unraveling the Self-Assembly of the XcpQ Secretin Periplasmic Domain Provides New Molecular Insights into Type II Secretion System Secreton Architecture and Dynamics. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | mBio, Vol. 8, Issue 5, Year 2017 |
| 掲載日 | 2017年10月17日 |
 著者 著者 | Badreddine Douzi / Nhung T T Trinh / Sandra Michel-Souzy / Aline Desmyter / Geneviève Ball / Pascale Barbier / Artemis Kosta / Eric Durand / Katrina T Forest / Christian Cambillau / Alain Roussel / Romé Voulhoux /   |
| PubMed 要旨 | The type II secretion system (T2SS) releases large folded exoproteins across the envelope of many Gram-negative pathogens. This secretion process therefore requires specific gating, interacting, and ...The type II secretion system (T2SS) releases large folded exoproteins across the envelope of many Gram-negative pathogens. This secretion process therefore requires specific gating, interacting, and dynamics properties mainly operated by a bipartite outer membrane channel called secretin. We have a good understanding of the structure-function relationship of the pore-forming C-terminal domain of secretins. In contrast, the high flexibility of their periplasmic N-terminal domain has been an obstacle in obtaining the detailed structural information required to uncover its molecular function. In , the Xcp T2SS plays an important role in bacterial virulence by its capacity to deliver a large panel of toxins and degradative enzymes into the surrounding environment. Here, we revealed that the N-terminal domain of XcpQ secretin spontaneously self-assembled into a hexamer of dimers independently of its C-terminal domain. Furthermore, and by using multidisciplinary approaches, we elucidate the structural organization of the XcpQ N domain and demonstrate that secretin flexibility at interdimer interfaces is mandatory for its function. Bacterial secretins are large homooligomeric proteins constituting the outer membrane pore-forming element of several envelope-embedded nanomachines essential in bacterial survival and pathogenicity. They comprise a well-defined membrane-embedded C-terminal domain and a modular periplasmic N-terminal domain involved in substrate recruitment and connection with inner membrane components. We are studying the XcpQ secretin of the T2SS present in the pathogenic bacterium Our data highlight the ability of the XcpQ N-terminal domain to spontaneously oligomerize into a hexamer of dimers. Further experiments revealed that this domain adopts different conformations essential for the T2SS secretion process. These findings provide new insights into the functional understanding of bacterial T2SS secretins. |
 リンク リンク |  mBio / mBio /  PubMed:29042493 / PubMed:29042493 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) / X線回折 |
| 解像度 | 2.9 - 30.8 Å |
| 構造データ |  EMDB-3641: 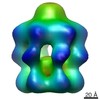 EMDB-3649: 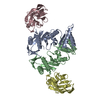 PDB-5mp2: 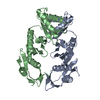 PDB-5ngi: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-HOH: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / T2SS / secretin / camedlid nanobody / Secretion system II / Pseudomonas aeruginosa / secretin N domain |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について





