+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | In situ architecture of neuronal α-Synuclein inclusions. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nat Commun, Vol. 12, Issue 1, Page 2110, Year 2021 |
| 掲載日 | 2021年4月14日 |
 著者 著者 | Victoria A Trinkaus / Irene Riera-Tur / Antonio Martínez-Sánchez / Felix J B Bäuerlein / Qiang Guo / Thomas Arzberger / Wolfgang Baumeister / Irina Dudanova / Mark S Hipp / F Ulrich Hartl / Rubén Fernández-Busnadiego /     |
| PubMed 要旨 | The molecular architecture of α-Synuclein (α-Syn) inclusions, pathognomonic of various neurodegenerative disorders, remains unclear. α-Syn inclusions were long thought to consist mainly of α-Syn ...The molecular architecture of α-Synuclein (α-Syn) inclusions, pathognomonic of various neurodegenerative disorders, remains unclear. α-Syn inclusions were long thought to consist mainly of α-Syn fibrils, but recent reports pointed to intracellular membranes as the major inclusion component. Here, we use cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) to image neuronal α-Syn inclusions in situ at molecular resolution. We show that inclusions seeded by α-Syn aggregates produced recombinantly or purified from patient brain consist of α-Syn fibrils crisscrossing a variety of cellular organelles. Using gold-labeled seeds, we find that aggregate seeding is predominantly mediated by small α-Syn fibrils, from which cytoplasmic fibrils grow unidirectionally. Detailed analysis of membrane interactions revealed that α-Syn fibrils do not contact membranes directly, and that α-Syn does not drive membrane clustering. Altogether, we conclusively demonstrate that neuronal α-Syn inclusions consist of α-Syn fibrils intermixed with membranous organelles, and illuminate the mechanism of aggregate seeding and cellular interaction. |
 リンク リンク |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:33854052 / PubMed:33854052 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (トモグラフィー) |
| 構造データ | 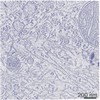 EMDB-11401: 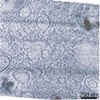 EMDB-11416: 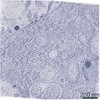 EMDB-11417: |
| 由来 |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について




