+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure and function of the Si3 insertion integrated into the trigger loop/helix of cyanobacterial RNA polymerase. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 121, Issue 8, Page e2311480121, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Feb 20, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | M Zuhaib Qayyum / Masahiko Imashimizu / Miron Leanca / Rishi K Vishwakarma / Amber Riaz-Bradley / Yulia Yuzenkova / Katsuhiko S Murakami /    |
| PubMed Abstract | Cyanobacteria and evolutionarily related chloroplasts of algae and plants possess unique RNA polymerases (RNAPs) with characteristics that distinguish them from canonical bacterial RNAPs. The largest ...Cyanobacteria and evolutionarily related chloroplasts of algae and plants possess unique RNA polymerases (RNAPs) with characteristics that distinguish them from canonical bacterial RNAPs. The largest subunit of cyanobacterial RNAP (cyRNAP) is divided into two polypeptides, β'1 and β'2, and contains the largest known lineage-specific insertion domain, Si3, located in the middle of the trigger loop and spanning approximately half of the β'2 subunit. In this study, we present the X-ray crystal structure of Si3 and the cryo-EM structures of the cyRNAP transcription elongation complex plus the NusG factor with and without incoming nucleoside triphosphate (iNTP) bound at the active site. Si3 has a well-ordered and elongated shape that exceeds the length of the main body of cyRNAP, fits into cavities of cyRNAP in the absence of iNTP bound at the active site and shields the binding site of secondary channel-binding proteins such as Gre and DksA. A small transition from the trigger loop to the trigger helix upon iNTP binding results in a large swing motion of Si3; however, this transition does not affect the catalytic activity of cyRNAP due to its minimal contact with cyRNAP, NusG, or DNA. This study provides a structural framework for understanding the evolutionary significance of these features unique to cyRNAP and chloroplast RNAP and may provide insights into the molecular mechanism of transcription in specific environment of photosynthetic organisms and organelle. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:38354263 / PubMed:38354263 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.79 - 3.06 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-40874, PDB-8syi: EMDB-42502, PDB-8urw:  PDB-8emb: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ZN: 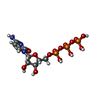 ChemComp-CTP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / RNA polymerase / Lineage specific insertion / trigger loop / Transcription regulation RNAP NusG cryo-EM / Transcription regulation / RNAP / NusG / cryo-EM |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers






 synechococcus elongatus (bacteria)
synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) thermosynechococcus vestitus bp-1 (bacteria)
thermosynechococcus vestitus bp-1 (bacteria)