+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure and mechanism of a eukaryotic ceramide synthase complex. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | EMBO J, Vol. 42, Issue 24, Page e114889, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | Dec 11, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | Tian Xie / Qi Fang / Zike Zhang / Yanfei Wang / Feitong Dong / Xin Gong /  |
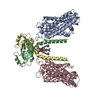
| PubMed Abstract | Ceramide synthases (CerS) catalyze ceramide formation via N-acylation of a sphingoid base with a fatty acyl-CoA and are attractive drug targets for treating numerous metabolic diseases and cancers. ...Ceramide synthases (CerS) catalyze ceramide formation via N-acylation of a sphingoid base with a fatty acyl-CoA and are attractive drug targets for treating numerous metabolic diseases and cancers. Here, we present the cryo-EM structure of a yeast CerS complex, consisting of a catalytic Lac1 subunit and a regulatory Lip1 subunit, in complex with C26-CoA substrate. The CerS holoenzyme exists as a dimer of Lac1-Lip1 heterodimers. Lac1 contains a hydrophilic reaction chamber and a hydrophobic tunnel for binding the CoA moiety and C26-acyl chain of C26-CoA, respectively. Lip1 interacts with both the transmembrane region and the last luminal loop of Lac1 to maintain the proper acyl chain binding tunnel. A lateral opening on Lac1 serves as a potential entrance for the sphingoid base substrate. Our findings provide a template for understanding the working mechanism of eukaryotic ceramide synthases and may facilitate the development of therapeutic CerS modulators. |
 External links External links |  EMBO J / EMBO J /  PubMed:37953642 / PubMed:37953642 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.09 - 3.85 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-35862, PDB-8izd: EMDB-35863, PDB-8izf: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-6PL: 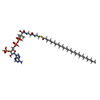 ChemComp-9NY: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / Substrate / Complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers