+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Cryo-EM structures of ClC-2 chloride channel reveal the blocking mechanism of its specific inhibitor AK-42. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 14, Issue 1, Page 3424, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | Jun 9, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | Tao Ma / Lei Wang / Anping Chai / Chao Liu / Wenqiang Cui / Shuguang Yuan / Shannon Wing Ngor Au / Liang Sun / Xiaokang Zhang / Zhenzhen Zhang / Jianping Lu / Yuanzhu Gao / Peiyi Wang / Zhifang Li / Yujie Liang / Horst Vogel / Yu Tian Wang / Daping Wang / Kaige Yan / Huawei Zhang /   |
| PubMed Abstract | ClC-2 transports chloride ions across plasma membranes and plays critical roles in cellular homeostasis. Its dysfunction is involved in diseases including leukodystrophy and primary aldosteronism. AK- ...ClC-2 transports chloride ions across plasma membranes and plays critical roles in cellular homeostasis. Its dysfunction is involved in diseases including leukodystrophy and primary aldosteronism. AK-42 was recently reported as a specific inhibitor of ClC-2. However, experimental structures are still missing to decipher its inhibition mechanism. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of apo ClC-2 and its complex with AK-42, both at 3.5 Å resolution. Residues S162, E205 and Y553 are involved in chloride binding and contribute to the ion selectivity. The side-chain of the gating glutamate E205 occupies the putative central chloride-binding site, indicating that our structure represents a closed state. Structural analysis, molecular dynamics and electrophysiological recordings identify key residues to interact with AK-42. Several AK-42 interacting residues are present in ClC-2 but not in other ClCs, providing a possible explanation for AK-42 specificity. Taken together, our results experimentally reveal the potential inhibition mechanism of ClC-2 inhibitor AK-42. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:37296152 / PubMed:37296152 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.5 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-34202, PDB-8gqu: |
| Chemicals | 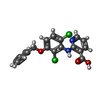 ChemComp-GH6: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / homo-dimer |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)