+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural and mechanistic basis for translation inhibition by macrolide and ketolide antibiotics. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 12, Issue 1, Page 4466, Year 2021 |
| Publish date | Jul 22, 2021 |
 Authors Authors | Bertrand Beckert / Elodie C Leroy / Shanmugapriya Sothiselvam / Lars V Bock / Maxim S Svetlov / Michael Graf / Stefan Arenz / Maha Abdelshahid / Britta Seip / Helmut Grubmüller / Alexander S Mankin / C Axel Innis / Nora Vázquez-Laslop / Daniel N Wilson /    |
| PubMed Abstract | Macrolides and ketolides comprise a family of clinically important antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis by binding within the exit tunnel of the bacterial ribosome. While these antibiotics are ...Macrolides and ketolides comprise a family of clinically important antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis by binding within the exit tunnel of the bacterial ribosome. While these antibiotics are known to interrupt translation at specific sequence motifs, with ketolides predominantly stalling at Arg/Lys-X-Arg/Lys motifs and macrolides displaying a broader specificity, a structural basis for their context-specific action has been lacking. Here, we present structures of ribosomes arrested during the synthesis of an Arg-Leu-Arg sequence by the macrolide erythromycin (ERY) and the ketolide telithromycin (TEL). Together with deep mutagenesis and molecular dynamics simulations, the structures reveal how ERY and TEL interplay with the Arg-Leu-Arg motif to induce translational arrest and illuminate the basis for the less stringent sequence-specific action of ERY over TEL. Because programmed stalling at the Arg/Lys-X-Arg/Lys motifs is used to activate expression of antibiotic resistance genes, our study also provides important insights for future development of improved macrolide antibiotics. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:34294725 / PubMed:34294725 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
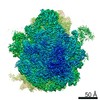
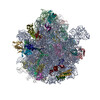
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.9 - 3.5 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-12573, PDB-7nso: EMDB-12574, PDB-7nsp: EMDB-12575, PDB-7nsq: |
| Chemicals | 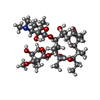 ChemComp-ERY: 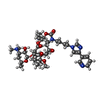 ChemComp-TEL: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / Antibiotic / ErmDL / Erythromycin / Macrolide / Stalling / Telithromycin |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers