+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Mechanism of pharmacochaperoning in a mammalian K channel revealed by cryo-EM. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Elife, Vol. 8, Year 2019 |
| Publish date | Jul 25, 2019 |
 Authors Authors | Gregory M Martin / Min Woo Sung / Zhongying Yang / Laura M Innes / Balamurugan Kandasamy / Larry L David / Craig Yoshioka / Show-Ling Shyng /  |
| PubMed Abstract | ATP-sensitive potassium (K) channels composed of a pore-forming Kir6.2 potassium channel and a regulatory ABC transporter sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) regulate insulin secretion in pancreatic β- ...ATP-sensitive potassium (K) channels composed of a pore-forming Kir6.2 potassium channel and a regulatory ABC transporter sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) regulate insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells to maintain glucose homeostasis. Mutations that impair channel folding or assembly prevent cell surface expression and cause congenital hyperinsulinism. Structurally diverse K inhibitors are known to act as pharmacochaperones to correct mutant channel expression, but the mechanism is unknown. Here, we compare cryoEM structures of a mammalian K channel bound to pharmacochaperones glibenclamide, repaglinide, and carbamazepine. We found all three drugs bind within a common pocket in SUR1. Further, we found the N-terminus of Kir6.2 inserted within the central cavity of the SUR1 ABC core, adjacent the drug binding pocket. The findings reveal a common mechanism by which diverse compounds stabilize the Kir6.2 N-terminus within SUR1's ABC core, allowing it to act as a firm 'handle' for the assembly of metastable mutant SUR1-Kir6.2 complexes. |
 External links External links |  Elife / Elife /  PubMed:31343405 / PubMed:31343405 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.65 - 4.55 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-20528, PDB-6pz9: EMDB-20530, PDB-6pza: EMDB-20533, PDB-6pzb: EMDB-20534, PDB-6pzc: EMDB-20535, PDB-6pzi: |
| Chemicals | 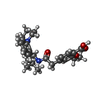 ChemComp-BJX:  ChemComp-ATP: 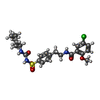 ChemComp-GBM: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / KATP / SUR1 / RPG / GBC / apo / carbamazepine / ATP |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





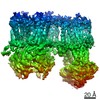
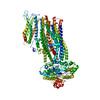

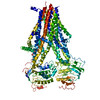
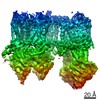

 cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster)
cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster)