+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Immunogenicity and structures of a rationally designed prefusion MERS-CoV spike antigen. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 114, Issue 35, Page E7348-E7357, Year 2017 |
| Publish date | Aug 29, 2017 |
 Authors Authors | Jesper Pallesen / Nianshuang Wang / Kizzmekia S Corbett / Daniel Wrapp / Robert N Kirchdoerfer / Hannah L Turner / Christopher A Cottrell / Michelle M Becker / Lingshu Wang / Wei Shi / Wing-Pui Kong / Erica L Andres / Arminja N Kettenbach / Mark R Denison / James D Chappell / Barney S Graham / Andrew B Ward / Jason S McLellan /  |
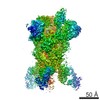
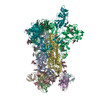
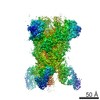
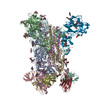
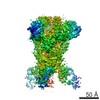
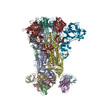
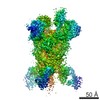
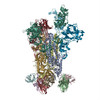
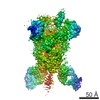
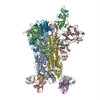
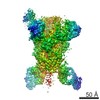
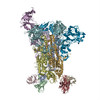
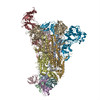
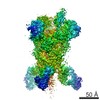
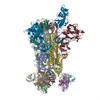
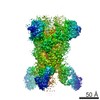
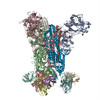
| PubMed Abstract | Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is a lineage C betacoronavirus that since its emergence in 2012 has caused outbreaks in human populations with case-fatality rates of ∼36%. ...Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is a lineage C betacoronavirus that since its emergence in 2012 has caused outbreaks in human populations with case-fatality rates of ∼36%. As in other coronaviruses, the spike (S) glycoprotein of MERS-CoV mediates receptor recognition and membrane fusion and is the primary target of the humoral immune response during infection. Here we use structure-based design to develop a generalizable strategy for retaining coronavirus S proteins in the antigenically optimal prefusion conformation and demonstrate that our engineered immunogen is able to elicit high neutralizing antibody titers against MERS-CoV. We also determined high-resolution structures of the trimeric MERS-CoV S ectodomain in complex with G4, a stem-directed neutralizing antibody. The structures reveal that G4 recognizes a glycosylated loop that is variable among coronaviruses and they define four conformational states of the trimer wherein each receptor-binding domain is either tightly packed at the membrane-distal apex or rotated into a receptor-accessible conformation. Our studies suggest a potential mechanism for fusion initiation through sequential receptor-binding events and provide a foundation for the structure-based design of coronavirus vaccines. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:28807998 / PubMed:28807998 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 1.57 - 11.5 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-8783: MERS S ectodomain trimer in complex with Fab of neutralizing antibody G4 EMDB-8784: MERS S ectodomain trimer in complex with Fab of neutralizing antibody G4 EMDB-8785: MERS S ectodomain trimer in complex with Fab of neutralizing antibody G4 EMDB-8786: MERS S ectodomain trimer in complex with Fab of neutralizing antibody G4 EMDB-8787: MERS S ectodomain trimer in complex with Fab of neutralizing antibody G4 EMDB-8788: MERS S ectodomain trimer in complex with Fab of neutralizing antibody G4 EMDB-8789: MERS S ectodomain trimer in complex with Fab of neutralizing antibody G4 EMDB-8790: MERS S ectodomain trimer in complex with Fab of neutralizing antibody G4 EMDB-8791: MERS S ectodomain trimer in complex with Fab of neutralizing antibody G4 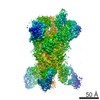 EMDB-8792: 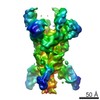 EMDB-8793:  PDB-5vyh: 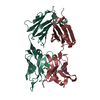 PDB-5vzr: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NAG:  ChemComp-FOL:  ChemComp-MPD:  ChemComp-IMD:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-GOL: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / fusion glycoprotein / virus / IMMUNE SYSTEM / antibody / neutralizing / Immunogen / peplomer / viral spike / MERS / MERS S protein / G4 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers