+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Ab initio structure determination from prion nanocrystals at atomic resolution by MicroED. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 113, Issue 40, Page 11232-11236, Year 2016 |
| Publish date | Oct 4, 2016 |
 Authors Authors | Michael R Sawaya / Jose Rodriguez / Duilio Cascio / Michael J Collazo / Dan Shi / Francis E Reyes / Johan Hattne / Tamir Gonen / David S Eisenberg /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Electrons, because of their strong interaction with matter, produce high-resolution diffraction patterns from tiny 3D crystals only a few hundred nanometers thick in a frozen-hydrated state. This ...Electrons, because of their strong interaction with matter, produce high-resolution diffraction patterns from tiny 3D crystals only a few hundred nanometers thick in a frozen-hydrated state. This discovery offers the prospect of facile structure determination of complex biological macromolecules, which cannot be coaxed to form crystals large enough for conventional crystallography or cannot easily be produced in sufficient quantities. Two potential obstacles stand in the way. The first is a phenomenon known as dynamical scattering, in which multiple scattering events scramble the recorded electron diffraction intensities so that they are no longer informative of the crystallized molecule. The second obstacle is the lack of a proven means of de novo phase determination, as is required if the molecule crystallized is insufficiently similar to one that has been previously determined. We show with four structures of the amyloid core of the Sup35 prion protein that, if the diffraction resolution is high enough, sufficiently accurate phases can be obtained by direct methods with the cryo-EM method microelectron diffraction (MicroED), just as in X-ray diffraction. The success of these four experiments dispels the concern that dynamical scattering is an obstacle to ab initio phasing by MicroED and suggests that structures of novel macromolecules can also be determined by direct methods. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:27647903 / PubMed:27647903 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (electron crystallography) |
| Resolution | 1 - 1.1 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-8196, PDB-5k2e: EMDB-8197, PDB-5k2f: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ZN: 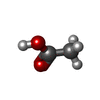 ChemComp-ACY:  ChemComp-HOH: 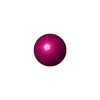 ChemComp-CD: 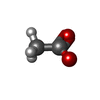 ChemComp-ACT: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL / amyloid / yeast prion |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers