+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structures and mechanisms of the Arabidopsis auxin transporter PIN3. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 609, Issue 7927, Page 616-621, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Aug 2, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Nannan Su / Aiqin Zhu / Xin Tao / Zhong Jie Ding / Shenghai Chang / Fan Ye / Yan Zhang / Cheng Zhao / Qian Chen / Jiangqin Wang / Chen Yu Zhou / Yirong Guo / Shasha Jiao / Sufen Zhang / Han Wen / Lixin Ma / Sheng Ye / Shao Jian Zheng / Fan Yang / Shan Wu / Jiangtao Guo /  |
| PubMed Abstract | The PIN-FORMED (PIN) protein family of auxin transporters mediates polar auxin transport and has crucial roles in plant growth and development. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of ...The PIN-FORMED (PIN) protein family of auxin transporters mediates polar auxin transport and has crucial roles in plant growth and development. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of PIN3 from Arabidopsis thaliana in the apo state and in complex with its substrate indole-3-acetic acid and the inhibitor N-1-naphthylphthalamic acid (NPA). A. thaliana PIN3 exists as a homodimer, and its transmembrane helices 1, 2 and 7 in the scaffold domain are involved in dimerization. The dimeric PIN3 forms a large, joint extracellular-facing cavity at the dimer interface while each subunit adopts an inward-facing conformation. The structural and functional analyses, along with computational studies, reveal the structural basis for the recognition of indole-3-acetic acid and NPA and elucidate the molecular mechanism of NPA inhibition on PIN-mediated auxin transport. The PIN3 structures support an elevator-like model for the transport of auxin, whereby the transport domains undergo up-down rigid-body motions and the dimerized scaffold domains remain static. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:35917926 PubMed:35917926 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.62 - 3.0 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-32568, PDB-7wks: EMDB-32570, PDB-7wkw: EMDB-33500, PDB-7xxb: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-E7O: 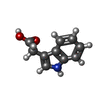 ChemComp-IAC: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / PIN-FORMED (PIN) protein / NPA |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers










