+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structures of metabotropic GABA receptor. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 584, Issue 7820, Page 310-314, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | Jun 24, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Makaía M Papasergi-Scott / Michael J Robertson / Alpay B Seven / Ouliana Panova / Jesper M Mathiesen / Georgios Skiniotis /   |
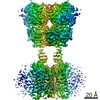
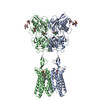
| PubMed Abstract | Stimulation of the metabotropic GABA receptor by γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) results in prolonged inhibition of neurotransmission, which is central to brain physiology. GABA belongs to family C of ...Stimulation of the metabotropic GABA receptor by γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) results in prolonged inhibition of neurotransmission, which is central to brain physiology. GABA belongs to family C of the G-protein-coupled receptors, which operate as dimers to transform synaptic neurotransmitter signals into a cellular response through the binding and activation of heterotrimeric G proteins. However, GABA is unique in its function as an obligate heterodimer in which agonist binding and G-protein activation take place on distinct subunits. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of heterodimeric and homodimeric full-length GABA receptors. Complemented by cellular signalling assays and atomistic simulations, these structures reveal that extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) of GABA has an essential role in relaying structural transitions by ordering the linker that connects the extracellular ligand-binding domain to the transmembrane region. Furthermore, the ECL2 of each of the subunits of GABA caps and interacts with the hydrophilic head of a phospholipid that occupies the extracellular half of the transmembrane domain, thereby providing a potentially crucial link between ligand binding and the receptor core that engages G proteins. These results provide a starting framework through which to decipher the mechanistic modes of signal transduction mediated by GABA dimers, and have important implications for rational drug design that targets these receptors. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:32580208 / PubMed:32580208 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.2 - 3.6 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-21533, PDB-6w2x: EMDB-21534, PDB-6w2y: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NAG:  ChemComp-L9Q:  ChemComp-SGG:  ChemComp-MG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / Inhibitor / Heterodimer / GPCR / Homodimer |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)