+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Receptor binding and priming of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 for membrane fusion. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 588, Issue 7837, Page 327-330, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | Sep 17, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Donald J Benton / Antoni G Wrobel / Pengqi Xu / Chloë Roustan / Stephen R Martin / Peter B Rosenthal / John J Skehel / Steven J Gamblin /   |
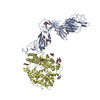
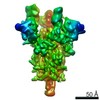
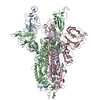
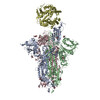
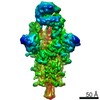
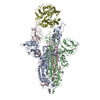
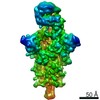
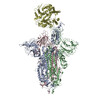
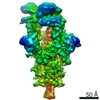
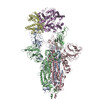
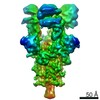
| PubMed Abstract | Infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is initiated by virus binding to the ACE2 cell-surface receptors, followed by fusion of the virus and cell membranes to ...Infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is initiated by virus binding to the ACE2 cell-surface receptors, followed by fusion of the virus and cell membranes to release the virus genome into the cell. Both receptor binding and membrane fusion activities are mediated by the virus spike glycoprotein. As with other class-I membrane-fusion proteins, the spike protein is post-translationally cleaved, in this case by furin, into the S1 and S2 components that remain associated after cleavage. Fusion activation after receptor binding is proposed to involve the exposure of a second proteolytic site (S2'), cleavage of which is required for the release of the fusion peptide. Here we analyse the binding of ACE2 to the furin-cleaved form of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein using cryo-electron microscopy. We classify ten different molecular species, including the unbound, closed spike trimer, the fully open ACE2-bound trimer and dissociated monomeric S1 bound to ACE2. The ten structures describe ACE2-binding events that destabilize the spike trimer, progressively opening up, and out, the individual S1 components. The opening process reduces S1 contacts and unshields the trimeric S2 core, priming the protein for fusion activation and dissociation of ACE2-bound S1 monomers. The structures also reveal refolding of an S1 subdomain after ACE2 binding that disrupts interactions with S2, which involves Asp614 and leads to the destabilization of the structure of S2 proximal to the secondary (S2') cleavage site. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:32942285 / PubMed:32942285 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.6 - 5.9 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-11681, PDB-7a91: EMDB-11682, PDB-7a92: EMDB-11683, PDB-7a93: EMDB-11684, PDB-7a94: EMDB-11685, PDB-7a95: EMDB-11686, PDB-7a96: EMDB-11687, PDB-7a97: EMDB-11688, PDB-7a98: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NAG:  ChemComp-ZN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / SARS-CoV-2 / Spike / Virus Glycoprotein / Coronavirus / ACE2 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers








 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
