+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure of DNA-CMG-Pol epsilon elucidates the roles of the non-catalytic polymerase modules in the eukaryotic replisome. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 9, Issue 1, Page 5061, Year 2018 |
| Publish date | Nov 29, 2018 |
 Authors Authors | Panchali Goswami / Ferdos Abid Ali / Max E Douglas / Julia Locke / Andrew Purkiss / Agnieszka Janska / Patrik Eickhoff / Anne Early / Andrea Nans / Alan M C Cheung / John F X Diffley / Alessandro Costa /  |
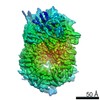
| PubMed Abstract | Eukaryotic origin firing depends on assembly of the Cdc45-MCM-GINS (CMG) helicase. A key step is the recruitment of GINS that requires the leading-strand polymerase Pol epsilon, composed of Pol2, ...Eukaryotic origin firing depends on assembly of the Cdc45-MCM-GINS (CMG) helicase. A key step is the recruitment of GINS that requires the leading-strand polymerase Pol epsilon, composed of Pol2, Dpb2, Dpb3, Dpb4. While a truncation of the catalytic N-terminal Pol2 supports cell division, Dpb2 and C-terminal Pol2 (C-Pol2) are essential for viability. Dpb2 and C-Pol2 are non-catalytic modules, shown or predicted to be related to an exonuclease and DNA polymerase, respectively. Here, we present the cryo-EM structure of the isolated C-Pol2/Dpb2 heterodimer, revealing that C-Pol2 contains a DNA polymerase fold. We also present the structure of CMG/C-Pol2/Dpb2 on a DNA fork, and find that polymerase binding changes both the helicase structure and fork-junction engagement. Inter-subunit contacts that keep the helicase-polymerase complex together explain several cellular phenotypes. At least some of these contacts are preserved during Pol epsilon-dependent CMG assembly on path to origin firing, as observed with DNA replication reconstituted in vitro. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:30498216 / PubMed:30498216 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 4.4 - 4.98 Å |
| Structure data | |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ZN:  ChemComp-AGS: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / Polymerase epsilon / DNA replication / enzyme / DNA polymerase / Helicase / Polymerase / AAA+ protein |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers