+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure and mechanism of the osmoregulated choline transporter BetT. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Sci Adv, Vol. 10, Issue 33, Page eado6229, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Aug 16, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Tianjiao Yang / Yuwei Nian / Huajian Lin / Jing Li / Xiang Lin / Tianming Li / Ruiying Wang / Longfei Wang / Gwyn A Beattie / Jinru Zhang / Minrui Fan /   |
| PubMed Abstract | The choline-glycine betaine pathway plays an important role in bacterial survival in hyperosmotic environments. Osmotic activation of the choline transporter BetT promotes the uptake of external ...The choline-glycine betaine pathway plays an important role in bacterial survival in hyperosmotic environments. Osmotic activation of the choline transporter BetT promotes the uptake of external choline for synthesizing the osmoprotective glycine betaine. Here, we report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of BetT in the apo and choline-bound states. Our structure shows that BetT forms a domain-swapped trimer with the C-terminal domain (CTD) of one protomer interacting with the transmembrane domain (TMD) of a neighboring protomer. The substrate choline is bound within a tryptophan prism at the central part of TMD. Together with functional characterization, our results suggest that in species, including the plant pathogen and the human pathogen , BetT is locked at a low-activity state through CTD-mediated autoinhibition in the absence of osmotic stress, and its hyperosmotic activation involves the release of this autoinhibition. |
 External links External links |  Sci Adv / Sci Adv /  PubMed:39141726 / PubMed:39141726 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.57 - 2.59 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-39121, PDB-8ybq: EMDB-39122, PDB-8ybr: |
| Chemicals | 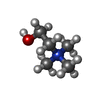 ChemComp-CHT:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | CHOLINE-BINDING PROTEIN / choline transporter |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers







 pseudomonas syringae (bacteria)
pseudomonas syringae (bacteria)