+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Molecular basis for the catalytic mechanism of human neutral sphingomyelinases 1 (hSMPD2). |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nat Commun, Vol. 14, Issue 1, Page 7755, Year 2023 |
| 掲載日 | 2023年11月27日 |
 著者 著者 | Jingbo Yi / Boya Qi / Jian Yin / Ruochong Li / Xudong Chen / Junhan Hu / Guohui Li / Sensen Zhang / Yuebin Zhang / Maojun Yang /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | Enzymatic breakdown of sphingomyelin by sphingomyelinase (SMase) is the main source of the membrane lipids, ceramides, which are involved in many cellular physiological processes. However, the full- ...Enzymatic breakdown of sphingomyelin by sphingomyelinase (SMase) is the main source of the membrane lipids, ceramides, which are involved in many cellular physiological processes. However, the full-length structure of human neutral SMase has not been resolved; therefore, its catalytic mechanism remains unknown. Here, we resolve the structure of human full-length neutral SMase, sphingomyelinase 1 (SMPD2), which reveals that C-terminal transmembrane helices contribute to dimeric architecture of hSMPD2 and that D111 - K116 loop domain is essential for substrate hydrolysis. Coupled with molecular docking, we clarify the binding pose of sphingomyelin, and site-directed mutagenesis further confirms key residues responsible for sphingomyelin binding. Hybrid quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) molecular dynamic (MD) simulations are utilized to elaborate the catalysis of hSMPD2 with the reported in vitro substrates, sphingomyelin and lyso-platelet activating fator (lyso-PAF). Our study provides mechanistic details that enhance our knowledge of lipid metabolism and may lead to an improved understanding of ceramide in disease and in cancer treatment. |
 リンク リンク |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:38012235 / PubMed:38012235 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.07 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-35948, PDB-8j2f: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-MG: 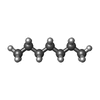 ChemComp-HP6: 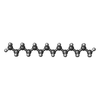 ChemComp-C14: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / enzyme |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について




 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト)