+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural Insights into the Distortion of the Ribosomal Small Subunit at Different Magnesium Concentrations. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Biomolecules, Vol. 13, Issue 3, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | Mar 20, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | Ting Yu / Junyi Jiang / Qianxi Yu / Xin Li / Fuxing Zeng /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Magnesium ions are abundant and play indispensable functions in the ribosome. A decrease in Mg concentration causes 70S ribosome dissociation and subsequent unfolding. Structural distortion at low Mg ...Magnesium ions are abundant and play indispensable functions in the ribosome. A decrease in Mg concentration causes 70S ribosome dissociation and subsequent unfolding. Structural distortion at low Mg concentrations has been observed in an immature pre50S, while the structural changes in mature subunits have not yet been studied. Here, we purified the 30S subunits of cells under various Mg concentrations and analyzed their structural distortion by cryo-electron microscopy. Upon systematically interrogating the structural heterogeneity within the 1 mM Mg dataset, we observed 30S particles with different levels of structural distortion in the decoding center, h17, and the 30S head. Our model showed that, when the Mg concentration decreases, the decoding center distorts, starting from h44 and followed by the shifting of h18 and h27, as well as the dissociation of ribosomal protein S12. Mg deficiency also eliminates the interactions between h17, h10, h15, and S16, resulting in the movement of h17 towards the tip of h6. More flexible structures were observed in the 30S head and platform, showing high variability in these regions. In summary, the structures resolved here showed several prominent distortion events in the decoding center and h17. The requirement for Mg in ribosomes suggests that the conformational changes reported here are likely shared due to a lack of cellular Mg in all domains of life. |
 External links External links |  Biomolecules / Biomolecules /  PubMed:36979501 / PubMed:36979501 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.96 - 4.98 Å |
| Structure data | 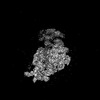 EMDB-34985: Structure of 30S ribosomal subunit at 2.5 mM Magnesium concentration 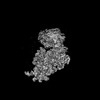 EMDB-34986: Structure of 30S ribosomal subunit at 10 mM Magnesium concentration 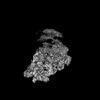 EMDB-34987: The global structure of 30S subunit at 1 mM Magnesium concentration 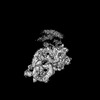 EMDB-34988: The structure of 30S subunit at 1 mM Magnesium concentration focused on h17 flexible 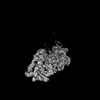 EMDB-34989: The stucture of 30S subunit at 1mM magnesium concentration focused on h17 out state 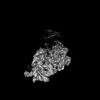 EMDB-34990: The structure of 30S subunit at 1 mM Magnesium concentration focused on h17in-2 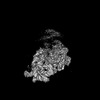 EMDB-34991: The global structure of 30S subunit at 1 mM Magnesium concentration focused on h17in |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




