+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Cryo-EM reveals an unprecedented binding site for Na1.7 inhibitors enabling rational design of potent hybrid inhibitors. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Elife, Vol. 12, Year 2023 |
| 掲載日 | 2023年3月28日 |
 著者 著者 | Marc Kschonsak / Christine C Jao / Christopher P Arthur / Alexis L Rohou / Philippe Bergeron / Daniel F Ortwine / Steven J McKerrall / David H Hackos / Lunbin Deng / Jun Chen / Tianbo Li / Peter S Dragovich / Matthew Volgraf / Matthew R Wright / Jian Payandeh / Claudio Ciferri / John C Tellis /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | The voltage-gated sodium (Na) channel Na1.7 has been identified as a potential novel analgesic target due to its involvement in human pain syndromes. However, clinically available Na channel-blocking ...The voltage-gated sodium (Na) channel Na1.7 has been identified as a potential novel analgesic target due to its involvement in human pain syndromes. However, clinically available Na channel-blocking drugs are not selective among the nine Na channel subtypes, Na1.1-Na1.9. Moreover, the two currently known classes of Na1.7 subtype-selective inhibitors (aryl- and acylsulfonamides) have undesirable characteristics that may limit their development. To this point understanding of the structure-activity relationships of the acylsulfonamide class of Na1.7 inhibitors, exemplified by the clinical development candidate , has been based solely on a single co-crystal structure of an arylsulfonamide inhibitor bound to voltage-sensing domain 4 (VSD4). To advance inhibitor design targeting the Na1.7 channel, we pursued high-resolution ligand-bound Na1.7-VSD4 structures using cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Here, we report that engages the Na1.7-VSD4 through an unexpected binding mode orthogonal to the arylsulfonamide inhibitor class binding pose, which identifies a previously unknown ligand binding site in Na channels. This finding enabled the design of a novel hybrid inhibitor series that bridges the aryl- and acylsulfonamide binding pockets and allows for the generation of molecules with substantially differentiated structures and properties. Overall, our study highlights the power of cryo-EM methods to pursue challenging drug targets using iterative and high-resolution structure-guided inhibitor design. This work also underscores an important role of the membrane bilayer in the optimization of selective Na channel modulators targeting VSD4. |
 リンク リンク |  Elife / Elife /  PubMed:36975198 / PubMed:36975198 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 2.2 - 3.1 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-28776, PDB-8f0p: EMDB-28777, PDB-8f0q: EMDB-28778, PDB-8f0r: EMDB-28779, PDB-8f0s: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-NAG: 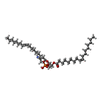 ChemComp-PEE:  ChemComp-Y01: 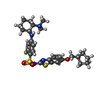 ChemComp-X7L:  ChemComp-HOH: 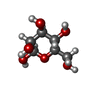 ChemComp-BMA: 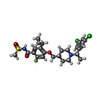 ChemComp-X7R: 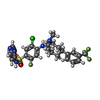 ChemComp-X7W: 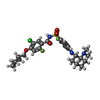 ChemComp-X80: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN/INHIBITOR / Ion channel / small molecule / inhibitor / MEMBRANE PROTEIN-INHIBITOR complex |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について










 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト) diguetia canities (クモ)
diguetia canities (クモ)