[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-28779: Structure of VSD4-NaV1.7-NaVPas channel chimera bound to the hybr... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of VSD4-NaV1.7-NaVPas channel chimera bound to the hybrid inhibitor GNE-9296 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Density modified map used for model refinements | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationaction potential propagation / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception / membrane depolarization during action potential / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / node of Ranvier / voltage-gated sodium channel complex / host cell presynaptic membrane / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / voltage-gated sodium channel activity ...action potential propagation / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception / membrane depolarization during action potential / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / node of Ranvier / voltage-gated sodium channel complex / host cell presynaptic membrane / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / behavioral response to pain / sodium channel regulator activity / neuronal action potential / sensory perception of pain / axon terminus / sodium ion transmembrane transport / post-embryonic development / circadian rhythm / response to toxic substance / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / toxin activity / inflammatory response / axon / extracellular region / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Diguetia canities (spider) Diguetia canities (spider) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kschonsak M / Jao CC / Arthur CP / Rohou AL / Bergeron P / Ortwine D / McKerall SJ / Hackos DH / Deng L / Chen J ...Kschonsak M / Jao CC / Arthur CP / Rohou AL / Bergeron P / Ortwine D / McKerall SJ / Hackos DH / Deng L / Chen J / Sutherlin D / Dragovich PS / Volgraf M / Wright MR / Payandeh J / Ciferri C / Tellis JC | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2023 Journal: Elife / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM reveals an unprecedented binding site for Na1.7 inhibitors enabling rational design of potent hybrid inhibitors. Authors: Marc Kschonsak / Christine C Jao / Christopher P Arthur / Alexis L Rohou / Philippe Bergeron / Daniel F Ortwine / Steven J McKerrall / David H Hackos / Lunbin Deng / Jun Chen / Tianbo Li / ...Authors: Marc Kschonsak / Christine C Jao / Christopher P Arthur / Alexis L Rohou / Philippe Bergeron / Daniel F Ortwine / Steven J McKerrall / David H Hackos / Lunbin Deng / Jun Chen / Tianbo Li / Peter S Dragovich / Matthew Volgraf / Matthew R Wright / Jian Payandeh / Claudio Ciferri / John C Tellis /  Abstract: The voltage-gated sodium (Na) channel Na1.7 has been identified as a potential novel analgesic target due to its involvement in human pain syndromes. However, clinically available Na channel-blocking ...The voltage-gated sodium (Na) channel Na1.7 has been identified as a potential novel analgesic target due to its involvement in human pain syndromes. However, clinically available Na channel-blocking drugs are not selective among the nine Na channel subtypes, Na1.1-Na1.9. Moreover, the two currently known classes of Na1.7 subtype-selective inhibitors (aryl- and acylsulfonamides) have undesirable characteristics that may limit their development. To this point understanding of the structure-activity relationships of the acylsulfonamide class of Na1.7 inhibitors, exemplified by the clinical development candidate , has been based solely on a single co-crystal structure of an arylsulfonamide inhibitor bound to voltage-sensing domain 4 (VSD4). To advance inhibitor design targeting the Na1.7 channel, we pursued high-resolution ligand-bound Na1.7-VSD4 structures using cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Here, we report that engages the Na1.7-VSD4 through an unexpected binding mode orthogonal to the arylsulfonamide inhibitor class binding pose, which identifies a previously unknown ligand binding site in Na channels. This finding enabled the design of a novel hybrid inhibitor series that bridges the aryl- and acylsulfonamide binding pockets and allows for the generation of molecules with substantially differentiated structures and properties. Overall, our study highlights the power of cryo-EM methods to pursue challenging drug targets using iterative and high-resolution structure-guided inhibitor design. This work also underscores an important role of the membrane bilayer in the optimization of selective Na channel modulators targeting VSD4. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
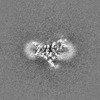
| Map data |  emd_28779.map.gz emd_28779.map.gz | 7.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28779-v30.xml emd-28779-v30.xml emd-28779.xml emd-28779.xml | 24.3 KB 24.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_28779.png emd_28779.png | 82.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28779_additional_1.map.gz emd_28779_additional_1.map.gz emd_28779_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28779_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28779_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28779_half_map_2.map.gz | 226.2 MB 49 MB 49 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28779 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28779 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28779 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28779 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8f0sMC  8f0pC  8f0qC  8f0rC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28779.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28779.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Density modified map used for model refinements | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.824 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
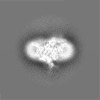
-Additional map: Non-modified, full map
| File | emd_28779_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Non-modified, full map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
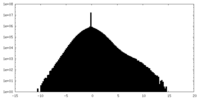
| Density Histograms |
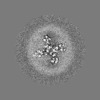
-Half map: half-map-1
| File | emd_28779_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-map-1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half-map-2
| File | emd_28779_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-map-2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : VSD4-NaV1.7-NaVPas channel chimera bound to the hybrid inhibitor ...
| Entire | Name: VSD4-NaV1.7-NaVPas channel chimera bound to the hybrid inhibitor GNE-9296 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: VSD4-NaV1.7-NaVPas channel chimera bound to the hybrid inhibitor ...
| Supramolecule | Name: VSD4-NaV1.7-NaVPas channel chimera bound to the hybrid inhibitor GNE-9296 type: complex / ID: 1 / Chimera: Yes / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 Details: Chimeric construct of human Nav1.7 VSD4 and the NavPaS channel from American cockroach Periplaneta americana |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Sodium channel protein PaFPC1,Sodium channel protein type 9 subun...
| Macromolecule | Name: Sodium channel protein PaFPC1,Sodium channel protein type 9 subunit alpha chimera type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 184.481906 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MWSHPQFEKG GGSGGGSGGS AWSHPQFEKG GSGGDYKDDD DKGGSGGDYK DDDDKMADNS PLIREERQRL FRPYTRAMLT APSAQPAKE NGKTEENKDN SRDKGRGANK DRDGSAHPDQ ALEQGSRLPA RMRNIFPAEL ASTPLEDFDP FYKNKKTFVV V TKAGDIFR ...String: MWSHPQFEKG GGSGGGSGGS AWSHPQFEKG GSGGDYKDDD DKGGSGGDYK DDDDKMADNS PLIREERQRL FRPYTRAMLT APSAQPAKE NGKTEENKDN SRDKGRGANK DRDGSAHPDQ ALEQGSRLPA RMRNIFPAEL ASTPLEDFDP FYKNKKTFVV V TKAGDIFR FSGEKSLWML DPFTPIRRVA ISTMVQPIFS YFIMITILIH CIFMIMPATQ TTYILELVFL SIYTIEVVVK VL ARGFILH PFAYLRDPWN WLDFLVTLIG YITLVVDLGH LYALRAFRVL RSWRTVTIVP GWRTIVDALS LSITSLKDLV LLL LFSLSV FALIGLQLFM GNLKHKCVKH FPADGSWGNF TDERWFNYTS NSSHWYIPDD WIEYPLCGNS SGAGMCPPGY TCLQ GYGGN PNYGYTSFDT FGWAFLSVFR LVTLDYWEDL YQLALRSAGP WHILFFIIVV FYGTFCFLNF ILAVVVMSYT HMVKR ADEE KAAERELKKE KKAASVANNT ANGQEQTTIE MNGDEAVVID NNDQAARQQS DPETPAPSVT QRLTDFLCVW DCCVPW QKL QGAIGAVVLS PFFELFIAVI IVLNITFMAL DHHDMNIEFE RILRTGNYIF TSIYIVEAVL KIIALSPKFY FKDSWNV FD FIIVVFAILE LGLEGVQGLS VFRSFRLLRV FRLAKFWPTL NNFMSVMTKS YGAFVNVMYV MFLLLFIFAI IGMQLFGM N YIDNMERFPD GDLPRWNFTD FLHSFMIVFR ALCGEWIESM WDCMLVGDWS CIPFFVAVFF VGNLVILNLL IALLLNNYG SFCTSPTSDE EDSKDEDALA QIVRIFKRFK PNLNAVKLSP MKPDSEDIVE SQEIQGNNIA DAEDVLAGEF PPDCCCNAFY KCFPSRPAR DSSVQRMWSN IRRVCFLLAK NKYFQKFVTA VLVITSVLLA LEDIYLPQRP VLVNITLYVD YVLTAFFVIE M IIMLFAVG FKKYFTSKWY WLDFIVVVAY LLNFVLMCAG IEALQTLRLL RVFRLFRPLS KVNGMQVVTS TLVEAVPHIF NV ILVGIFF WLVFAIMGVQ LFAGKFYKCV DENSTVLSHE ITMDRNDCLH ENYTWENSPM NFDHVGNAYL SLLQVATFKG WLQ IMNDAI DSREVHKQPI RETNIYMYLY FIFFIVFGSF FILKLFVCIL IDIFRQQRRK AEGLSATDSR TQLIYRRAVM RTMS AKPVK RIPKPGNKIQ GCIFDLVTNQ AFDISIMVLI CLNMVTMMVE KEGQSQHMTE VLYWINVVFI ILFTGECVLK LISLR HYYF TVGWNIFDFV VVIISIVGMF LADLIETYFV SPTLFRVIRL ARIGRILRLV KGAKGIRLLL LALRKALRTL FNVSFL LFV IMFVYAVFGM EFFMHIRDAG AIDDVYNFKT FGQSIILLFQ LATSAGWDGV YFAIANEEDC RAPDHELGYP GNCGSRA LG IAYLVSYLII TCLVVINMYA AVILDYVLEV YEDSKEGLTD DDYDMFFEVW QQFDPEATQY IRYDQLSELL EALQPPLQ V QKPNKYKILS MNIPICKDDH IFYKDVLEAL VKDVFSRRGS PVEAGDVQAP NVDEAEYKPV SSTLQRQREE YCVRLIQNA WRKHKQQN |
-Macromolecule #2: Beta-diguetoxin-Dc1a
| Macromolecule | Name: Beta-diguetoxin-Dc1a / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Diguetia canities (spider) Diguetia canities (spider) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8.240277 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: HHHHHHGENL YFQGSAKDGD VEGPAGCKKY DVECDSGECC QKQYLWYKWR PLDCRCLKSG FFSSKCVCRD V |
-Macromolecule #5: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #6: 5-chloro-4-(cyclopentylmethoxy)-N-(4-{[(1S,2S)-2-(dimethylamino)c...
| Macromolecule | Name: 5-chloro-4-(cyclopentylmethoxy)-N-(4-{[(1S,2S)-2-(dimethylamino)cyclohexyl]amino}-2-fluorobenzene-1-sulfonyl)-2-fluorobenzamide type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: X80 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 570.091 Da |
| Chemical component information | 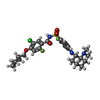 ChemComp-X80: |
-Macromolecule #7: 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine
| Macromolecule | Name: 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PEE |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 744.034 Da |
| Chemical component information | 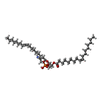 ChemComp-PEE: |
-Macromolecule #8: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: Y01 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 486.726 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-Y01: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| |||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R2/2 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 200 / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 10 sec. | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | |||||||||||||||
| Details | The sample was monodisperse. The sample was crosslinked with 0.05% glutaraldehyde for 10 minutes at RT, then quenched with 1M Tris pH7.0. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Average exposure time: 10.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8f0s: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)