+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure, substrate binding and activity of a unique AAA+ protein: the BrxL phage restriction factor. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nucleic Acids Res, Vol. 51, Issue 8, Page 3513-3528, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | May 8, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | Betty W Shen / Lindsey A Doyle / Rachel Werther / Abigail A Westburg / Daniel P Bies / Stephanie I Walter / Yvette A Luyten / Richard D Morgan / Barry L Stoddard / Brett K Kaiser /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Bacteriophage exclusion ('BREX') systems are multi-protein complexes encoded by a variety of bacteria and archaea that restrict phage by an unknown mechanism. One BREX factor, termed BrxL, has been ...Bacteriophage exclusion ('BREX') systems are multi-protein complexes encoded by a variety of bacteria and archaea that restrict phage by an unknown mechanism. One BREX factor, termed BrxL, has been noted to display sequence similarity to various AAA+ protein factors including Lon protease. In this study we describe multiple CryoEM structures of BrxL that demonstrate it to be a chambered, ATP-dependent DNA binding protein. The largest BrxL assemblage corresponds to a dimer of heptamers in the absence of bound DNA, versus a dimer of hexamers when DNA is bound in its central pore. The protein displays DNA-dependent ATPase activity, and ATP binding promotes assembly of the complex on DNA. Point mutations within several regions of the protein-DNA complex alter one or more in vitro behaviors and activities, including ATPase activity and ATP-dependent association with DNA. However, only the disruption of the ATPase active site fully eliminates phage restriction, indicating that other mutations can still complement BrxL function within the context of an otherwise intact BREX system. BrxL displays significant structural homology to MCM subunits (the replicative helicase in archaea and eukaryotes), implying that it and other BREX factors may collaborate to disrupt initiation of phage DNA replication. |
 External links External links |  Nucleic Acids Res / Nucleic Acids Res /  PubMed:36794719 / PubMed:36794719 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.25 - 3.63 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-28244, PDB-8emc: EMDB-28248, PDB-8emh:  PDB-8eil: |
| Chemicals | 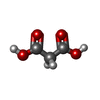 ChemComp-MLA: 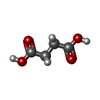 ChemComp-SIN:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / helicase / phage restriction / LonP/RadA homolog / BREX / ANTIMICROBIAL PROTEIN / phage restriction factor / AAA+ protein. BrxL / AAA+ protein |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers






 Acinetobacter (bacteria)
Acinetobacter (bacteria)