+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Cryo-electron microscopy structures of VCP/p97 reveal a new mechanism of oligomerization regulation. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | iScience, Vol. 24, Issue 11, Page 103310, Year 2021 |
| Publish date | Nov 19, 2021 |
 Authors Authors | Guimei Yu / Yunpeng Bai / Kunpeng Li / Ovini Amarasinghe / Wen Jiang / Zhong-Yin Zhang /  |
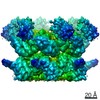
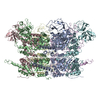
| PubMed Abstract | VCP/p97 is an evolutionarily conserved AAA+ ATPase important for cellular homeostasis. Previous studies suggest that VCP predominantly exists as a homohexamer. Here, we performed structural and ...VCP/p97 is an evolutionarily conserved AAA+ ATPase important for cellular homeostasis. Previous studies suggest that VCP predominantly exists as a homohexamer. Here, we performed structural and biochemical characterization of VCP dodecamer, an understudied state of VCP. The structure revealed an apo nucleotide status that has rarely been captured, a tail-to-tail assembly of two hexamers, and the up-elevated N-terminal domains akin to that seen in the ATP-bound hexamer. Further analyses elucidated a nucleotide status-dependent dodecamerization mechanism, where nucleotide dissociation from the D2 AAA domains induces and promotes VCP dodecamerization. In contrast, nucleotide-free D1 AAA domains are associated with the up-rotation of N-terminal domains, which may prime D1 for ATP binding. These results therefore reveal new nucleotide status-dictated intra- and interhexamer conformational changes and suggest that modulation of D2 domain nucleotide occupancy may serve as a mechanism in controlling VCP oligomeric states. |
 External links External links |  iScience / iScience /  PubMed:34765927 / PubMed:34765927 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.7 - 4.2 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-22675, PDB-7k56: EMDB-22676, PDB-7k57: EMDB-22678, PDB-7k59: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN / HYDROLASE / AAA ATPase / ATP hydrolysis / segregase |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



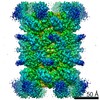
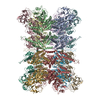
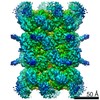
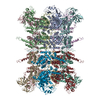
 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)