+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Direct visualization of degradation microcompartments at the ER membrane. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 117, Issue 2, Page 1069-1080, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | Jan 14, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Sahradha Albert / Wojciech Wietrzynski / Chia-Wei Lee / Miroslava Schaffer / Florian Beck / Jan M Schuller / Patrice A Salomé / Jürgen M Plitzko / Wolfgang Baumeister / Benjamin D Engel /   |
| PubMed Abstract | To promote the biochemical reactions of life, cells can compartmentalize molecular interaction partners together within separated non-membrane-bound regions. It is unknown whether this strategy is ...To promote the biochemical reactions of life, cells can compartmentalize molecular interaction partners together within separated non-membrane-bound regions. It is unknown whether this strategy is used to facilitate protein degradation at specific locations within the cell. Leveraging in situ cryo-electron tomography to image the native molecular landscape of the unicellular alga , we discovered that the cytosolic protein degradation machinery is concentrated within ∼200-nm foci that contact specialized patches of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane away from the ER-Golgi interface. These non-membrane-bound microcompartments exclude ribosomes and consist of a core of densely clustered 26S proteasomes surrounded by a loose cloud of Cdc48. Active proteasomes in the microcompartments directly engage with putative substrate at the ER membrane, a function canonically assigned to Cdc48. Live-cell fluorescence microscopy revealed that the proteasome clusters are dynamic, with frequent assembly and fusion events. We propose that the microcompartments perform ER-associated degradation, colocalizing the degradation machinery at specific ER hot spots to enable efficient protein quality control. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:31882451 / PubMed:31882451 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (tomography) / EM (subtomogram averaging) |
| Resolution | 17.24 - 35.0 Å |
| Structure data |  EMDB-10409: 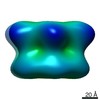 EMDB-10410: 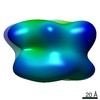 EMDB-10411:  EMDB-3932:  EMDB-3933:  EMDB-3934:  EMDB-3935: |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




