+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure of the human ClC-1 chloride channel. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | PLoS Biol, Vol. 17, Issue 4, Page e3000218, Year 2019 |
| Publish date | Apr 25, 2019 |
 Authors Authors | Kaituo Wang / Sarah Spruce Preisler / Liying Zhang / Yanxiang Cui / Julie Winkel Missel / Christina Grønberg / Kamil Gotfryd / Erik Lindahl / Magnus Andersson / Kirstine Calloe / Pascal F Egea / Dan Arne Klaerke / Michael Pusch / Per Amstrup Pedersen / Z Hong Zhou / Pontus Gourdon /     |
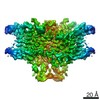
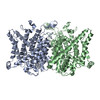
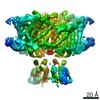
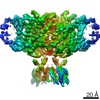
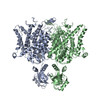
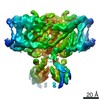
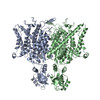
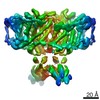
| PubMed Abstract | ClC-1 protein channels facilitate rapid passage of chloride ions across cellular membranes, thereby orchestrating skeletal muscle excitability. Malfunction of ClC-1 is associated with myotonia ...ClC-1 protein channels facilitate rapid passage of chloride ions across cellular membranes, thereby orchestrating skeletal muscle excitability. Malfunction of ClC-1 is associated with myotonia congenita, a disease impairing muscle relaxation. Here, we present the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of human ClC-1, uncovering an architecture reminiscent of that of bovine ClC-K and CLC transporters. The chloride conducting pathway exhibits distinct features, including a central glutamate residue ("fast gate") known to confer voltage-dependence (a mechanistic feature not present in ClC-K), linked to a somewhat rearranged central tyrosine and a narrower aperture of the pore toward the extracellular vestibule. These characteristics agree with the lower chloride flux of ClC-1 compared with ClC-K and enable us to propose a model for chloride passage in voltage-dependent CLC channels. Comparison of structures derived from protein studied in different experimental conditions supports the notion that pH and adenine nucleotides regulate ClC-1 through interactions between the so-called cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS) domains and the intracellular vestibule ("slow gating"). The structure also provides a framework for analysis of mutations causing myotonia congenita and reveals a striking correlation between mutated residues and the phenotypic effect on voltage gating, opening avenues for rational design of therapies against ClC-1-related diseases. |
 External links External links |  PLoS Biol / PLoS Biol /  PubMed:31022181 / PubMed:31022181 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.63 - 4.34 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-4645, PDB-6qv6: EMDB-4646: CryoEM structure of the human ClC-1 chloride channel, CBS state 1 EMDB-4647, PDB-6qvc: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / chloride channel / CLC1 / CLCN1 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)