+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Epitope-based vaccine design yields fusion peptide-directed antibodies that neutralize diverse strains of HIV-1. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Med, Vol. 24, Issue 6, Page 857-867, Year 2018 |
| Publish date | Jun 4, 2018 |
 Authors Authors | Kai Xu / Priyamvada Acharya / Rui Kong / Cheng Cheng / Gwo-Yu Chuang / Kevin Liu / Mark K Louder / Sijy O'Dell / Reda Rawi / Mallika Sastry / Chen-Hsiang Shen / Baoshan Zhang / Tongqing Zhou / Mangaiarkarasi Asokan / Robert T Bailer / Michael Chambers / Xuejun Chen / Chang W Choi / Venkata P Dandey / Nicole A Doria-Rose / Aliaksandr Druz / Edward T Eng / S Katie Farney / Kathryn E Foulds / Hui Geng / Ivelin S Georgiev / Jason Gorman / Kurt R Hill / Alexander J Jafari / Young D Kwon / Yen-Ting Lai / Thomas Lemmin / Krisha McKee / Tiffany Y Ohr / Li Ou / Dongjun Peng / Ariana P Rowshan / Zizhang Sheng / John-Paul Todd / Yaroslav Tsybovsky / Elise G Viox / Yiran Wang / Hui Wei / Yongping Yang / Amy F Zhou / Rui Chen / Lu Yang / Diana G Scorpio / Adrian B McDermott / Lawrence Shapiro / Bridget Carragher / Clinton S Potter / John R Mascola / Peter D Kwong /  |
| PubMed Abstract | A central goal of HIV-1 vaccine research is the elicitation of antibodies capable of neutralizing diverse primary isolates of HIV-1. Here we show that focusing the immune response to exposed N- ...A central goal of HIV-1 vaccine research is the elicitation of antibodies capable of neutralizing diverse primary isolates of HIV-1. Here we show that focusing the immune response to exposed N-terminal residues of the fusion peptide, a critical component of the viral entry machinery and the epitope of antibodies elicited by HIV-1 infection, through immunization with fusion peptide-coupled carriers and prefusion stabilized envelope trimers, induces cross-clade neutralizing responses. In mice, these immunogens elicited monoclonal antibodies capable of neutralizing up to 31% of a cross-clade panel of 208 HIV-1 strains. Crystal and cryoelectron microscopy structures of these antibodies revealed fusion peptide conformational diversity as a molecular explanation for the cross-clade neutralization. Immunization of guinea pigs and rhesus macaques induced similarly broad fusion peptide-directed neutralizing responses, suggesting translatability. The N terminus of the HIV-1 fusion peptide is thus a promising target of vaccine efforts aimed at eliciting broadly neutralizing antibodies. |
 External links External links |  Nat Med / Nat Med /  PubMed:29867235 / PubMed:29867235 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
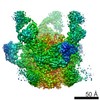
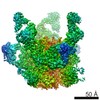
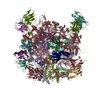
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 1.55 - 19.6 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-7459, PDB-6cde: EMDB-7460, PDB-6cdi: 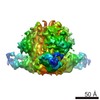 EMDB-8420: 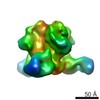 EMDB-8421:  EMDB-8422: 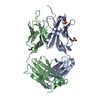 PDB-5tkj: 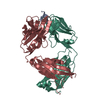 PDB-5tkk:  PDB-6cdm:  PDB-6cdo:  PDB-6cdp: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-SO4:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-NAG: 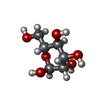 ChemComp-MAN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / Neutralizing / antibody / fusion-peptide / complex / mouse / VIRAL PROTEIN / HIV-1 Env / BG505 SOSIP / fusion peptide / VRC03 / PGT122 / vFP20.01 / vFP16.02 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
 human immunodeficiency virus 1
human immunodeficiency virus 1
