+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure and operation of the DNA-translocating type I DNA restriction enzymes. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Genes Dev, Vol. 26, Issue 1, Page 92-9104, Year 2012 |
| Publish date | Jan 1, 2012 |
 Authors Authors | Christopher K Kennaway / James E N Taylor / Chun Feng Song / Wojciech Potrzebowski / William Nicholson / John H White / Anna Swiderska / Agnieszka Obarska-Kosinska / Philip Callow / Laurie P Cooper / Gareth A Roberts / Jean-Baptiste Artero / Janusz M Bujnicki / John Trinick / G Geoff Kneale / David T F Dryden /    |
| PubMed Abstract | Type I DNA restriction/modification (RM) enzymes are molecular machines found in the majority of bacterial species. Their early discovery paved the way for the development of genetic engineering. ...Type I DNA restriction/modification (RM) enzymes are molecular machines found in the majority of bacterial species. Their early discovery paved the way for the development of genetic engineering. They control (restrict) the influx of foreign DNA via horizontal gene transfer into the bacterium while maintaining sequence-specific methylation (modification) of host DNA. The endonuclease reaction of these enzymes on unmethylated DNA is preceded by bidirectional translocation of thousands of base pairs of DNA toward the enzyme. We present the structures of two type I RM enzymes, EcoKI and EcoR124I, derived using electron microscopy (EM), small-angle scattering (neutron and X-ray), and detailed molecular modeling. DNA binding triggers a large contraction of the open form of the enzyme to a compact form. The path followed by DNA through the complexes is revealed by using a DNA mimic anti-restriction protein. The structures reveal an evolutionary link between type I RM enzymes and type II RM enzymes. |
 External links External links |  Genes Dev / Genes Dev /  PubMed:22215814 / PubMed:22215814 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 20.0 - 35.0 Å |
| Structure data |  EMDB-1890: 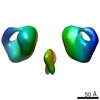 EMDB-1891: 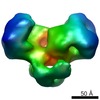 EMDB-1892: 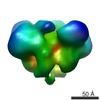 EMDB-1893: |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 Enterobacteria phage T7 (virus)
Enterobacteria phage T7 (virus)