+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Electron microscopic analysis of KvAP voltage-dependent K+ channels in an open conformation. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 430, Issue 7001, Page 806-810, Year 2004 |
| Publish date | Aug 12, 2004 |
 Authors Authors | Qiu-Xing Jiang / Da-Neng Wang / Roderick MacKinnon /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Voltage-dependent ion channels serve as field-effect transistors by opening a gate in response to membrane voltage changes. The gate's response to voltage is mediated by voltage sensors, which are ...Voltage-dependent ion channels serve as field-effect transistors by opening a gate in response to membrane voltage changes. The gate's response to voltage is mediated by voltage sensors, which are arginine-containing structures that must move with respect to the membrane electric field. We have analysed by electron microscopy a voltage-dependent K(+) channel from Aeropyrum pernix (KvAP). Fab fragments were attached to 'voltage sensor paddles' and identified in the electron microscopy map at 10.5 A resolution. The extracellular surface location of the Fab fragments in the map is consistent with the membrane-depolarized, open conformation of the channel in electrophysiological experiments. Comparison of the map with a crystal structure demonstrates that the voltage sensor paddles are 'up' (that is, near the channel's extracellular surface) and situated at the protein-lipid interface. This finding supports the hypothesis that in response to changes in voltage the sensors move at the protein-lipid interface rather than in a gating pore surrounded by protein. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:15306816 PubMed:15306816 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 10.5 Å |
| Structure data | 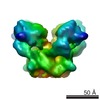 EMDB-1094: |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




 Aeropyrum pernix (archaea)
Aeropyrum pernix (archaea)
