+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Bacterial reverse transcriptase synthesizes long poly(A)-rich cDNA for antiphage defense. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Science, Vol. 388, Issue 6753, Page eads4639, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Jun 19, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Xin-Yi Song / Yushan Xia / Jun-Tao Zhang / Yu-Jun Liu / Hua Qi / Xin-Yang Wei / Hailiang Hu / Yu Xia / Xue Liu / Ying-Fei Ma / Ning Jia /  |
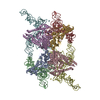
| PubMed Abstract | Prokaryotic defense-associated reverse transcriptases (DRTs) were recently identified with antiviral functions; however, their functional mechanisms remain largely unexplored. Here we show that DRT9 ...Prokaryotic defense-associated reverse transcriptases (DRTs) were recently identified with antiviral functions; however, their functional mechanisms remain largely unexplored. Here we show that DRT9 forms a hexameric complex with its upstream noncoding RNA (ncRNA) to mediate antiphage defense by inducing cell growth arrest through abortive infection. Upon phage infection, the phage-encoded ribonucleotide reductase NrdAB complex increases intracellular deoxyadenosine triphosphate levels, activating DRT9 to synthesize long, polyadenylate [poly(A)]-rich single-stranded complementary DNA (cDNA), which likely sequesters the essential phage single-stranded DNA binding (SSB) protein and disrupts phage propagation. We further determined the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the DRT9-ncRNA hexamer complex, providing mechanistic insights into its cDNA synthesis. These findings highlight the diversity of RT-based antiviral defense mechanisms, expand our understanding of RT biological functions, and provide a structural basis for developing DRT9-based biotechnological tools. |
 External links External links |  Science / Science /  PubMed:40310939 PubMed:40310939 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.59 - 2.62 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-60724, PDB-9ioa: EMDB-60725, PDB-9iob: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | ANTIVIRAL PROTEIN/RNA / RNA BINDING / PROTEIN-RNA COMPLEX / ANTIVIRAL PROTEIN-RNA complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About EMN Papers
About EMN Papers