[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
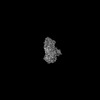
Yorodumi- EMDB-45563: Cryo-EM structure of myosin-1c bound to F-actin in the ADP-A state -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of myosin-1c bound to F-actin in the ADP-A state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | F-actin / myosin / myosin-1c / cellular motility / cryo-EM / actomyosin. / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus / stereocilium membrane / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Cam-PDE 1 activation / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Sodium/Calcium exchangers ...positive regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus / stereocilium membrane / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Cam-PDE 1 activation / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / Calmodulin induced events / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / eNOS activation / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / Protein methylation / RAF activation / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / RAS processing / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / Ca2+ pathway / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / Smooth Muscle Contraction / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / PKA activation / vesicle transport along actin filament / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / Platelet degranulation / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / Stimuli-sensing channels / B-WICH complex / Ion homeostasis / stereocilium / myosin complex / protein targeting to membrane / vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / microfilament motor activity / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / presynaptic endocytosis / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / tropomyosin binding / myosin heavy chain binding / calcineurin-mediated signaling / troponin I binding / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / mesenchyme migration / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / filamentous actin / actin filament bundle / brush border / microvillus / striated muscle thin filament / protein phosphatase activator activity / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / adenylate cyclase binding / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin monomer binding / positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane / catalytic complex / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / detection of calcium ion / lateral plasma membrane / calcium channel inhibitor activity / cellular response to interferon-beta / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / stress fiber / skeletal muscle fiber development / phagocytic vesicle / titin binding / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / sperm midpiece / calcium channel complex / calyx of Held / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / actin filament polymerization / adenylate cyclase activator activity / regulation of heart rate / sarcomere / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / basal plasma membrane / regulation of cytokinesis / filopodium / spindle microtubule / actin filament / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |    | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chavali SS / Sindelar CV / Ostap ME | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025Title: High-resolution structures of Myosin-IC reveal a unique actin-binding orientation, ADP release pathway, and power stroke trajectory. Authors: Sai Shashank Chavali / Peter J Carman / Henry Shuman / E Michael Ostap / Charles V Sindelar /  Abstract: Myosin-IC (myo1c) is a class-I myosin that supports transport and remodeling of the plasma membrane and membrane-bound vesicles. Like other members of the myosin family, its biochemical kinetics are ...Myosin-IC (myo1c) is a class-I myosin that supports transport and remodeling of the plasma membrane and membrane-bound vesicles. Like other members of the myosin family, its biochemical kinetics are altered in response to changes in mechanical loads that resist the power stroke. However, myo1c is unique in that the primary force-sensitive kinetic transition is the isomerization that follows ATP binding, not ADP release as in other slow myosins. Myo1c also powers actin gliding along curved paths, propelling actin filaments in leftward circles. To understand the origins of this unique force-sensing and motile behavior, we solved actin-bound myo1c cryo-EM structures in the presence and absence of ADP. Our structures reveal that in contrast with other myosins, the myo1c lever arm swing is skewed, partly due to a different actin interface that reorients the motor domain on actin. The structures also reveal unique nucleotide-dependent behavior of both the nucleotide pocket as well as an element called the N-terminal extension (NTE). We incorporate these observations into a model that explains why force primarily regulates ATP binding in myo1c, rather than ADP release as in other myosins. Integrating our cryo-EM data with available crystallography structures allows the modeling of full-length myo1c during force generation, supplying insights into its role in membrane remodeling. These results highlight how relatively minor sequence differences in members of the myosin superfamily can significantly alter power stroke geometry and force-sensing properties, with important implications for biological function. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_45563.map.gz emd_45563.map.gz | 1.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-45563-v30.xml emd-45563-v30.xml emd-45563.xml emd-45563.xml | 19.4 KB 19.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_45563_fsc.xml emd_45563_fsc.xml | 9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_45563.png emd_45563.png | 53.3 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_45563_msk_1.map emd_45563_msk_1.map | 64 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-45563.cif.gz emd-45563.cif.gz | 7.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_45563_half_map_1.map.gz emd_45563_half_map_1.map.gz emd_45563_half_map_2.map.gz emd_45563_half_map_2.map.gz | 200.4 MB 200.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45563 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45563 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45563 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45563 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_45563_validation.pdf.gz emd_45563_validation.pdf.gz | 675.1 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_45563_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_45563_full_validation.pdf.gz | 674.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_45563_validation.xml.gz emd_45563_validation.xml.gz | 19.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_45563_validation.cif.gz emd_45563_validation.cif.gz | 25.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-45563 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-45563 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-45563 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-45563 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9cfuMC  9cfvC  9cfwC  9cfxC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_45563.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_45563.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.346 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
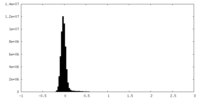
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_45563_msk_1.map emd_45563_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_45563_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_45563_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of myosin-1c with F-actin
| Entire | Name: Complex of myosin-1c with F-actin |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of myosin-1c with F-actin
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of myosin-1c with F-actin / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 220 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.862613 KDa |
| Sequence | String: DEDETTALVC DNGSGLVKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IEHGIITNWD DMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPTLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNV PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVLDSGDGV T HNVPIYEG ...String: DEDETTALVC DNGSGLVKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IEHGIITNWD DMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPTLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNV PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVLDSGDGV T HNVPIYEG YALPHAIMRL DLAGRDLTDY LMKILTERGY SFVTTAEREI VRDIKEKLCY VALDFENEMA TAASSSSLEK SY ELPDGQV ITIGNERFRC PETLFQPSFI GMESAGIHET TYNSIMKCDI DIRKDLYANN VMSGGTTMYP GIADRMQKEI TAL APSTMK IKIIAPPERK YSVWIGGSIL ASLSTFQQMW ITKQEYDEAG PSIVHRKCF UniProtKB: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle |
-Macromolecule #2: Unconventional myosin-Ic
| Macromolecule | Name: Unconventional myosin-Ic / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 92.064203 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  unidentified baculovirus unidentified baculovirus |
| Sequence | String: MESALTARDR VGVQDFVLLE NFTSEAAFIE NLRRRFRENL IYTYIGPVLV SVNPYRDLQI YSRQHMERYR GVSFYEVPPH LFAVADTVY RALRTERRDQ AVMISGESGA GKTEATKRLL QFYAETCPAP ERGGAVRDRL LQSNPVLEAF GNAKTLRNDN S SRFGKYMD ...String: MESALTARDR VGVQDFVLLE NFTSEAAFIE NLRRRFRENL IYTYIGPVLV SVNPYRDLQI YSRQHMERYR GVSFYEVPPH LFAVADTVY RALRTERRDQ AVMISGESGA GKTEATKRLL QFYAETCPAP ERGGAVRDRL LQSNPVLEAF GNAKTLRNDN S SRFGKYMD VQFDFKGAPV GGHILSYLLE KSRVVHQNHG ERNFHVFYQL LEGGEEETLR RLGLERNPQS YLYLVKGQCA KV SSINDKS DWKVMRKALS VIDFTEDEVE DLLSIVASVL HLGNIHFAAD EDSNAQVTTE NQLKYLTRLL GVEGTTLREA LTH RKIIAK GEELLSPLNL EQAAYARDAL AKAVYSRTFT WLVRKINRSL ASKDAESPSW RSTTVLGLLD IYGFEVFQHN SFEQ FCINY CNEKLQQLFI ELTLKSEQEE YEAEGIAWEP VQYFNNKIIC DLVEEKFKGI ISILDEECLR PGEATDLTFL EKLED TVKP HPHFLTHKLA DQKTRKSLDR GEFRLLHYAG EVTYSVTGFL DKNNDLLFRN LKETMCSSMN PIMAQCFDKS ELSDKK RPE TVATQFKMSL LQLVEILRSK EPAYIRCIKP NDAKQPGRFD EVLIRHQVKY LGLMENLRVR RAGFAYRRKY EAFLQRY KS LCPETWPMWA GRPQDGVAVL VRHLGYKPEE YKMGRTKIFI RFPKTLFATE DSLEVRRQSL ATKIQAAWRG FHWRQKFL R VKRSAICIQS WWRGTLGRRK AAKRKWAAQT IRRLIRGFIL RHSPRCGGLN DIFEAQKIEW HEAADYKDDD DK UniProtKB: Unconventional myosin-Ic |
-Macromolecule #3: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.723365 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  unidentified baculovirus unidentified baculovirus |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTA UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Macromolecule #4: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 52.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)