[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-44942: Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase with factor IX propeptide a... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
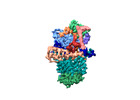
| Title | Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase with factor IX propeptide and partially carboxylated glutamate-rich region and with vitamin K hydroquinone and calcium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GGCX / VKGC / Vitamin K / VKCFD / Hemophilia B / Warfarin / Carboxylation / Blood Coagulaton / Calcium homeostasis / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / LYASE-SUBSTRATE complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpeptidyl-glutamate 4-carboxylase / gamma-glutamyl carboxylase activity / Defective F9 secretion / coagulation factor IXa / Defective gamma-carboxylation of F9 / vitamin binding / vitamin K metabolic process / Defective F9 activation / Defective factor IX causes thrombophilia / Defective cofactor function of FVIIIa variant ...peptidyl-glutamate 4-carboxylase / gamma-glutamyl carboxylase activity / Defective F9 secretion / coagulation factor IXa / Defective gamma-carboxylation of F9 / vitamin binding / vitamin K metabolic process / Defective F9 activation / Defective factor IX causes thrombophilia / Defective cofactor function of FVIIIa variant / Defective F9 variant does not activate FX / zymogen activation / Extrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / Protein hydroxylation / Transport of gamma-carboxylated protein precursors from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus / Gamma-carboxylation of protein precursors / Removal of aminoterminal propeptides from gamma-carboxylated proteins / Intrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / protein maturation / protein modification process / Golgi lumen / blood coagulation / : / endopeptidase activity / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / serine-type endopeptidase activity / calcium ion binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / proteolysis / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / metal ion binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li W / Liu B / Cao Q | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 7 items United States, 7 items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2025 Journal: Nature / Year: 2025Title: Molecular basis of vitamin-K-driven γ-carboxylation at the membrane interface. Authors: Qing Cao / Aaron Ammerman / Mierxiati Saimi / Zongtao Lin / Guomin Shen / Huaping Chen / Jie Sun / Mengqi Chai / Shixuan Liu / Fong-Fu Hsu / Andrzej M Krezel / Michael L Gross / Jinbin Xu / ...Authors: Qing Cao / Aaron Ammerman / Mierxiati Saimi / Zongtao Lin / Guomin Shen / Huaping Chen / Jie Sun / Mengqi Chai / Shixuan Liu / Fong-Fu Hsu / Andrzej M Krezel / Michael L Gross / Jinbin Xu / Benjamin A Garcia / Bin Liu / Weikai Li /   Abstract: The γ-carboxylation of glutamate residues enables Ca-mediated membrane assembly of protein complexes that support broad physiological functions, including haemostasis, calcium homeostasis, immune ...The γ-carboxylation of glutamate residues enables Ca-mediated membrane assembly of protein complexes that support broad physiological functions, including haemostasis, calcium homeostasis, immune response and endocrine regulation. Modulating γ-carboxylation levels provides prevalent treatments for haemorrhagic and thromboembolic diseases. This unique post-translational modification requires vitamin K hydroquinone (KH) to drive highly demanding reactions catalysed by the membrane-integrated γ-carboxylase (VKGC). Here, to decipher the underlying mechanisms, we determined cryo-electron microscopy structures of human VKGC in unbound form, with KH and four haemostatic and non-haemostatic proteins possessing propeptides and glutamate-rich domains in different carboxylation states. VKGC recognizes substrate proteins through knob-and-hole interactions with propeptides, thereby bringing tethered glutamate-containing segments for processive carboxylation within a large chamber that provides steric control. Propeptide binding also triggers a global conformational change to signal VKGC activation. Through sequential deprotonation and KH epoxidation, VKGC generates a free hydroxide ion as an exceptionally strong base that is required to deprotonate the γ-carbon of glutamate for CO addition. The diffusion of this superbase-protected and guided by a sealed hydrophobic tunnel-elegantly resolves the challenge of coupling KH epoxidation to γ-carboxylation across the membrane interface. These structural insights and extensive functional experiments advance membrane enzymology and propel the development of treatments for γ-carboxylation disorders. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44942.map.gz emd_44942.map.gz | 63 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44942-v30.xml emd-44942-v30.xml emd-44942.xml emd-44942.xml | 28 KB 28 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_44942_fsc.xml emd_44942_fsc.xml | 10.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_44942.png emd_44942.png | 42.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44942.cif.gz emd-44942.cif.gz | 7.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44942_additional_1.map.gz emd_44942_additional_1.map.gz emd_44942_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44942_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44942_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44942_half_map_2.map.gz | 64.1 MB 116.1 MB 116.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44942 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44942 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44942 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44942 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_44942_validation.pdf.gz emd_44942_validation.pdf.gz | 858.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_44942_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_44942_full_validation.pdf.gz | 858.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_44942_validation.xml.gz emd_44942_validation.xml.gz | 18.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_44942_validation.cif.gz emd_44942_validation.cif.gz | 24.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44942 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44942 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44942 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44942 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9bvrMC  9bvkC  9bvlC  9bvmC  9bvoC  9bvpC  9bvqC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44942.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44942.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.88533 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_44942_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_44942_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_44942_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase with factor IX propeptide a...
| Entire | Name: Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase with factor IX propeptide and partially carboxylated glutamate-rich region and with vitamin K hydroquinone and calcium |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase with factor IX propeptide a...
| Supramolecule | Name: Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase with factor IX propeptide and partially carboxylated glutamate-rich region and with vitamin K hydroquinone and calcium type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 110 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase
| Macromolecule | Name: Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: peptidyl-glutamate 4-carboxylase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 85.00568 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: GPRQDSRIGK LLGFEWTDLS SWRRLVTLLN RPTDPASLAV FRFLFGFLMV LDIPQERGLS SLDRKYLDGL DVCRFPLLDA LRPLPLDWM YLVYTIMFLG ALGMMLGLCY RISCVLFLLP YWYVFLLDKT SWNNHSYLYG LLAFQLTFMD ANHYWSVDGL L NAHRRNAH ...String: GPRQDSRIGK LLGFEWTDLS SWRRLVTLLN RPTDPASLAV FRFLFGFLMV LDIPQERGLS SLDRKYLDGL DVCRFPLLDA LRPLPLDWM YLVYTIMFLG ALGMMLGLCY RISCVLFLLP YWYVFLLDKT SWNNHSYLYG LLAFQLTFMD ANHYWSVDGL L NAHRRNAH VPLWNYAVLR GQIFIVYFIA GVKKLDADWV EGYSMEYLSR HWLFSPFKLL LSEELTSLLV VHWGGLLLDL SA GFLLFFD VSRSIGLFFV SYFHCMNSQL FSIGMFSYVM LASSPLFCSP EWPRKLVSYC PRRLQQLLPL KAAPQPSVSC VYK RSRGKS GQKPGLRHQL GAAFTLLYLL EQLFLPYSHF LTQGYNNWTN GLYGYSWDMM VHSRSHQHVK ITYRDGRTGE LGYL NPGVF TQSRRWKDHA DMLKQYATCL SRLLPKYNVT EPQIYFDIWV SINDRFQQRI FDPRVDIVQA AWSPFQRTSW VQPLL MDLS PWRAKLQEIK SSLDNHTEVV FIADFPGLHL ENFVSEDLGN TSIQLLQGEV TVELVAEQKN QTLREGEKMQ LPAGEY HKV YTTSPSPSCY MYVYVNTTEL ALEQDLAYLQ ELKEKVENGS ETGPLPPELQ PLLEGEVKGG PEPTPLVQTF LRRQQRL QE IERRRNTPFH ERFFRFLLRK LYVFRRSFLM TCISLRNLIL GRPSLEQLAQ EVTYANLRPF EAVGELNPSN TDSSHSNP P ESNPDPVHSE F UniProtKB: Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase |
-Macromolecule #2: Coagulation factor IX
| Macromolecule | Name: Coagulation factor IX / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: coagulation factor IXa |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 7.802636 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: TVFLDHENAN KILNRPKRYN SGKLEEFVQG NLERECMEEK CSFEEAREVF ENTERTTEFW KQYV UniProtKB: Coagulation factor IX |
-Macromolecule #4: vitamin K1 hydroquinone
| Macromolecule | Name: vitamin K1 hydroquinone / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: A1AVC |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 452.712 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: (4S,7R)-4-HYDROXY-N,N,N-TRIMETHYL-9-OXO-7-[(PALMITOYLOXY)METHYL]-...
| Macromolecule | Name: (4S,7R)-4-HYDROXY-N,N,N-TRIMETHYL-9-OXO-7-[(PALMITOYLOXY)METHYL]-3,5,8-TRIOXA-4-PHOSPHAHEXACOSAN-1-AMINIUM 4-OXIDE type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: 6PL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 763.1 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-6PL: |
-Macromolecule #6: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Support film - Film thickness: 10 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.039 kPa | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 283.15 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Min: 63.0 K / Max: 77.0 K |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 4092 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 5760 pixel / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 4992 / Average electron dose: 54.8 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-9bvr: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)