+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
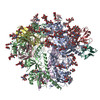
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of mAb8-24 bound to 426c.WITO.TM.SOSIP | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HIV / antibody / IMMUNE SYSTEM | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 / Human immunodeficiency virus 1 /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hurlburt NK / Pancera M | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2024 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2024Title: Short CDRL1 in intermediate VRC01-like mAbs is not sufficient to overcome key glycan barriers on HIV-1 Env. Authors: Parul Agrawal / Maria L Knudsen / Anna MacCamy / Nicholas K Hurlburt / Arineh Khechaduri / Kelsey R Salladay / Gargi M Kher / Latha Kallur Siddaramaiah / Andrew B Stuart / Ilja Bontjer / ...Authors: Parul Agrawal / Maria L Knudsen / Anna MacCamy / Nicholas K Hurlburt / Arineh Khechaduri / Kelsey R Salladay / Gargi M Kher / Latha Kallur Siddaramaiah / Andrew B Stuart / Ilja Bontjer / Xiaoying Shen / David Montefiori / Harry B Gristick / Pamela J Bjorkman / Rogier W Sanders / Marie Pancera / Leonidas Stamatatos /   Abstract: VRC01-class broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) have been isolated from people with HIV-1, but they have not yet been elicited by vaccination. They are extensively somatically mutated and ...VRC01-class broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) have been isolated from people with HIV-1, but they have not yet been elicited by vaccination. They are extensively somatically mutated and sometimes accumulate CDRL1 deletions. Such indels may allow VRC01-class antibodies to accommodate the glycans expressed on a conserved N276 N-linked glycosylation site in loop D of the gp120 subunit. These glycans constitute a major obstacle in the development of VRC01-class antibodies, as unmutated antibody forms are unable to accommodate them. Although immunizations of knock-in mice expressing human VRC01-class B-cell receptors (BCRs) with specifically designed Env-derived immunogens lead to the accumulation of somatic mutations in VRC01-class BCRs, CDRL1 deletions are rarely observed, and the elicited antibodies display narrow neutralizing activities. The lack of broad neutralizing potential could be due to the absence of deletions, the lack of appropriate somatic mutations, or both. To address this point, we modified our previously determined prime-boost immunization with a germline-targeting immunogen nanoparticle (426c.Mod.Core), followed by a heterologous core nanoparticle (HxB2.WT.Core), by adding a final boost with a cocktail of various stabilized soluble Env trimers. We isolated VRC01-like antibodies with extensive somatic mutations and, in one case, a seven-amino acid CDRL1 deletion. We generated chimeric antibodies that combine the vaccine-elicited somatic mutations with CDRL1 deletions present in human mature VRC01 bnAbs. We observed that CDRL1 indels did not improve the neutralizing antibody activities. Our study indicates that CDRL1 length by itself is not sufficient for the broadly neutralizing phenotype of this class of antibodies. IMPORTANCE: HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibodies will be a key component of an effective HIV-1 vaccine, as they prevent viral acquisition. Over the past decade, numerous broadly neutralizing ...IMPORTANCE: HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibodies will be a key component of an effective HIV-1 vaccine, as they prevent viral acquisition. Over the past decade, numerous broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) have been isolated from people with HIV. Despite an in-depth knowledge of their structures, epitopes, ontogenies, and, in a few rare cases, their maturation pathways during infection, bnAbs have, so far, not been elicited by vaccination. This necessitates the identification of key obstacles that prevent their elicitation by immunization and overcoming them. Here we examined whether CDRL1 shortening is a prerequisite for the broadly neutralizing potential of VRC01-class bnAbs, which bind within the CD4 receptor binding site of Env. Our findings indicate that CDRL1 shortening by itself is important but not sufficient for the acquisition of neutralization breadth, and suggest that particular combinations of amino acid mutations, not elicited so far by vaccination, are most likely required for the development of such a feature. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44510.map.gz emd_44510.map.gz | 110.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44510-v30.xml emd-44510-v30.xml emd-44510.xml emd-44510.xml | 21.5 KB 21.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_44510_fsc.xml emd_44510_fsc.xml | 17.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_44510.png emd_44510.png | 88.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44510.cif.gz emd-44510.cif.gz | 6.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44510_additional_1.map.gz emd_44510_additional_1.map.gz emd_44510_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44510_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44510_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44510_half_map_2.map.gz | 107.5 MB 200.6 MB 200.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44510 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44510 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44510 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44510 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_44510_validation.pdf.gz emd_44510_validation.pdf.gz | 965.4 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_44510_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_44510_full_validation.pdf.gz | 964.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_44510_validation.xml.gz emd_44510_validation.xml.gz | 21.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_44510_validation.cif.gz emd_44510_validation.cif.gz | 28 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44510 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44510 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44510 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44510 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44510.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44510.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.122 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Unsharpened Map
| File | emd_44510_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened Map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B
| File | emd_44510_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A
| File | emd_44510_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of 426c.WITO.TM.SOSIP bound to three mAb 8-24 Fabs
| Entire | Name: Complex of 426c.WITO.TM.SOSIP bound to three mAb 8-24 Fabs |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of 426c.WITO.TM.SOSIP bound to three mAb 8-24 Fabs
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of 426c.WITO.TM.SOSIP bound to three mAb 8-24 Fabs type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 210 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: 426c.WITO.TM.SOSIP
| Macromolecule | Name: 426c.WITO.TM.SOSIP / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Human immunodeficiency virus 1 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 69.535422 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: AENLWVTVYY GVPVWKEAKT TLFCASDAKA YEKEVHNVWA THACVPTDPN PQEVVLENVT ENFNMWKNDM VDQMQEDVIS IWDQSLKPC VKLTPLCVTL HCTNVTISST NGSTANVTMR EEMKNCSFNT TTVIRDKIQK EYALFYKLDI VPIEGKNTNT G YRLINCNT ...String: AENLWVTVYY GVPVWKEAKT TLFCASDAKA YEKEVHNVWA THACVPTDPN PQEVVLENVT ENFNMWKNDM VDQMQEDVIS IWDQSLKPC VKLTPLCVTL HCTNVTISST NGSTANVTMR EEMKNCSFNT TTVIRDKIQK EYALFYKLDI VPIEGKNTNT G YRLINCNT STCTQACPKV TFDPIPIHYC APAGYAILKC NNKTFNGKGP CNNVSTVQCT HGIKPVVSTQ LLLNGSLAEE EI VIRSKNL ADNAKIIIVQ LNKSVEIVCT RPNNNTRRSI RIGPGQTFYA TDIIGDIRQA YCNISGRNWS EAVNQVKKKL KEH FPHKNI SFQSSSGGDL EITTHSFNCG GEFFYCNTSG LFNDTISNAT IMLPCRIKQI INMWQEVGKC IYAPPIKGNI TCKS DITGL LLLRDGGNTA NNAEIFRPGG GDMRDNWRSE LYKYKVVKIE PLGVAPTRCK RRVVGRRRRR RAVGIGAVFL VFLGA AGST MGAASMTLTV QARNLLSGIV QQQSNLLRAP EAQQHLLKLT VWGIKQLQAR VLAVERYLRD QQLLGIWGCS GKLICC TNV PWNSSWSNRN LSEIWDNMTW LQWDKEISNY TQIIYGLLEE SQNQQEKNEQ DLLALD |
-Macromolecule #2: Fv domain of heavy chain of mAb 8-24
| Macromolecule | Name: Fv domain of heavy chain of mAb 8-24 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.560518 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: QVQLVQSGPE VKEPGASVRV SCKATGYTFT DHFIHWVRQA PGQGLDWMGW INPFRGGTNY PQKFQGRVTM TRDTSFTTAY MELNRLRSD DTAVYFCARG KNSDYNWDFQ HWGQGTLVTV SSASTKGPSV FPLAPSSKST SGGTAALGCL VKDYFPEPVT V SWNSGALT ...String: QVQLVQSGPE VKEPGASVRV SCKATGYTFT DHFIHWVRQA PGQGLDWMGW INPFRGGTNY PQKFQGRVTM TRDTSFTTAY MELNRLRSD DTAVYFCARG KNSDYNWDFQ HWGQGTLVTV SSASTKGPSV FPLAPSSKST SGGTAALGCL VKDYFPEPVT V SWNSGALT SGVHTFPAVL QSSGLYSLSS VVTVPSSSLG TQTYICNVNH KPSNTKVDKR VEPKSCDKTH HHHHH |
-Macromolecule #3: Fv domain of light chain of mAb 8-24
| Macromolecule | Name: Fv domain of light chain of mAb 8-24 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.049486 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: DIVMSQSPSS LAVSLGERIT LSCKSSLTLI YSYNGENYLA WYQQKPGQSP KLLIYSTSTR ESGVPDRFTG SGSGTDFTLT ISSVKAEDL AVYYCQQYEY FGGGTKLEIK RTVAAPSVFI FPPSDEQLKS GTASVVCLLN NFYPREAKVQ WKVDNALQSG N SQESVTEQ ...String: DIVMSQSPSS LAVSLGERIT LSCKSSLTLI YSYNGENYLA WYQQKPGQSP KLLIYSTSTR ESGVPDRFTG SGSGTDFTLT ISSVKAEDL AVYYCQQYEY FGGGTKLEIK RTVAAPSVFI FPPSDEQLKS GTASVVCLLN NFYPREAKVQ WKVDNALQSG N SQESVTEQ DSKDSTYSLS STLTLSKADY EKHKVYACEV TH |
-Macromolecule #8: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 21 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R2/2 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 200 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 36000 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)