[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-40187: Representative cryo-electron tomogram of pRLB-540 mixed with lipo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
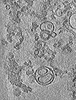
| Title | Representative cryo-electron tomogram of pRLB-540 mixed with liposomes, acidified to pH 5.5 and plunge frozen after 60s incubation. | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-electron tomogram of pRLB-540 mixed with liposomes (pH 5.5, 60s incubation) | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | pH-activated / lipid / lytic / liposome / LIPID BINDING PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Biological species | synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||
| Method | electron tomography / cryo EM | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Croft JT / Lee KK | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, European Union, 3 items United States, European Union, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Protein Sci / Year: 2023 Journal: Protein Sci / Year: 2023Title: De novo design of monomeric helical bundles for pH-controlled membrane lysis. Authors: Nicolas Goldbach / Issa Benna / Basile I M Wicky / Jacob T Croft / Lauren Carter / Asim K Bera / Hannah Nguyen / Alex Kang / Banumathi Sankaran / Erin C Yang / Kelly K Lee / David Baker /   Abstract: Targeted intracellular delivery via receptor-mediated endocytosis requires the delivered cargo to escape the endosome to prevent lysosomal degradation. This can in principle be achieved by membrane ...Targeted intracellular delivery via receptor-mediated endocytosis requires the delivered cargo to escape the endosome to prevent lysosomal degradation. This can in principle be achieved by membrane lysis tightly restricted to endosomal membranes upon internalization to avoid general membrane insertion and lysis. Here, we describe the design of small monomeric proteins with buried histidine containing pH-responsive hydrogen bond networks and membrane permeating amphipathic helices. Of the 30 designs that were experimentally tested, all expressed in Escherichia coli, 13 were monomeric with the expected secondary structure, and 4 designs disrupted artificial liposomes in a pH-dependent manner. Mutational analysis showed that the buried histidine hydrogen bond networks mediate pH-responsiveness and control lysis of model membranes within a very narrow range of pH (6.0-5.5) with almost no lysis occurring at neutral pH. These tightly controlled lytic monomers could help mediate endosomal escape in designed targeted delivery platforms. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_40187.map.gz emd_40187.map.gz | 317.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-40187-v30.xml emd-40187-v30.xml emd-40187.xml emd-40187.xml | 9.7 KB 9.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_40187.png emd_40187.png | 141 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-40187.cif.gz emd-40187.cif.gz | 4.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40187 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40187 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40187 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40187 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_40187_validation.pdf.gz emd_40187_validation.pdf.gz | 519.8 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_40187_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_40187_full_validation.pdf.gz | 519.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_40187_validation.xml.gz emd_40187_validation.xml.gz | 5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_40187_validation.cif.gz emd_40187_validation.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40187 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40187 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40187 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40187 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_40187.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 534.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS SIGNED BYTE Download / File: emd_40187.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 534.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS SIGNED BYTE | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-electron tomogram of pRLB-540 mixed with liposomes (pH 5.5, 60s incubation) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.7728 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : pRLB-540 mixed with DOPC lipids (pH 8.0)
| Entire | Name: pRLB-540 mixed with DOPC lipids (pH 8.0) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: pRLB-540 mixed with DOPC lipids (pH 8.0)
| Supramolecule | Name: pRLB-540 mixed with DOPC lipids (pH 8.0) / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | electron tomography |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 5.5 Component:
Details: TBS pH 8.0 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 4 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | |||||||||
| Sectioning | Other: NO SECTIONING |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average exposure time: 0.3 sec. / Average electron dose: 2.32 e/Å2 / Details: Total tomogram dose 95 e-/A^2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source: OTHER |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: OTHER / Nominal defocus max: 4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 2.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 64000 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Software - Name: EMAN2 (ver. 2.99) / Number images used: 41 |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller