[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-37742: Cryo-EM structure of CUL2-RBX1-ELOB-ELOC-FEM1B bound with the C-d... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
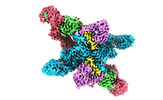
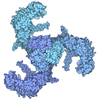
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of CUL2-RBX1-ELOB-ELOC-FEM1B bound with the C-degron of CUX1 (conformation 1) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | E3 ubiquitin ligase / Pro/C-degron / LIGASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / epithelial cell maturation involved in prostate gland development / Intra-Golgi traffic / branching involved in prostate gland morphogenesis / intra-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / cullin-RING-type E3 NEDD8 transferase / NEDD8 transferase activity / cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / cellular response to chemical stress ...regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / epithelial cell maturation involved in prostate gland development / Intra-Golgi traffic / branching involved in prostate gland morphogenesis / intra-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / cullin-RING-type E3 NEDD8 transferase / NEDD8 transferase activity / cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / cellular response to chemical stress / Cul7-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the C-end degron rule pathway / target-directed miRNA degradation / elongin complex / Loss of Function of FBXW7 in Cancer and NOTCH1 Signaling / VCB complex / regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / positive regulation of protein autoubiquitination / death receptor binding / protein neddylation / NEDD8 ligase activity / Cul5-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / negative regulation of response to oxidative stress / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / SCF ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul2-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul4B-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / negative regulation of type I interferon production / SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / ubiquitin ligase complex scaffold activity / Cul3-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / Prolactin receptor signaling / protein monoubiquitination / Pausing and recovery of Tat-mediated HIV elongation / Tat-mediated HIV elongation arrest and recovery / cullin family protein binding / HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Pausing and recovery of HIV elongation / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / ubiquitin-like ligase-substrate adaptor activity / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat / Formation of HIV elongation complex in the absence of HIV Tat / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / positive regulation of TORC1 signaling / post-translational protein modification / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus / Regulation of BACH1 activity / transcription corepressor binding / T cell activation / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / Degradation of DVL / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / Negative regulation of NOTCH4 signaling / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / Vif-mediated degradation of APOBEC3G / Hedgehog 'on' state / Degradation of GLI2 by the proteasome / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / Inactivation of CSF3 (G-CSF) signaling / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / Oxygen-dependent proline hydroxylation of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha / Transcription-Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER) / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Evasion by RSV of host interferon responses / NOTCH1 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 PEST Domain Mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD+PEST Domain Mutants / Regulation of expression of SLITs and ROBOs / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / Interleukin-1 signaling / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / Orc1 removal from chromatin / protein polyubiquitination / Regulation of RAS by GAPs / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / cellular response to UV / Regulation of RUNX2 expression and activity / MAPK cascade / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.38 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen X / Zhang K / Xu C | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Mechanism of Ψ-Pro/C-degron recognition by the CRL2 ubiquitin ligase. Authors: Xinyan Chen / Anat Raiff / Shanshan Li / Qiong Guo / Jiahai Zhang / Hualin Zhou / Richard T Timms / Xuebiao Yao / Stephen J Elledge / Itay Koren / Kaiming Zhang / Chao Xu /     Abstract: The E3 ligase-degron interaction determines the specificity of the ubiquitin‒proteasome system. We recently discovered that FEM1B, a substrate receptor of Cullin 2-RING ligase (CRL2), recognizes C- ...The E3 ligase-degron interaction determines the specificity of the ubiquitin‒proteasome system. We recently discovered that FEM1B, a substrate receptor of Cullin 2-RING ligase (CRL2), recognizes C-degrons containing a C-terminal proline. By solving several cryo-EM structures of CRL2 bound to different C-degrons, we elucidate the dimeric assembly of the complex. Furthermore, we reveal distinct dimerization states of unmodified and neddylated CRL2 to uncover the NEDD8-mediated activation mechanism of CRL2. Our research also indicates that, FEM1B utilizes a bipartite mechanism to recognize both the C-terminal proline and an upstream aromatic residue within the substrate. These structural findings, complemented by in vitro ubiquitination and in vivo cell-based assays, demonstrate that CRL2-mediated polyubiquitination and subsequent protein turnover depend on both FEM1B-degron interactions and the dimerization state of the E3 ligase complex. Overall, this study deepens our molecular understanding of how Cullin-RING E3 ligase substrate selection mediates protein turnover. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_37742.map.gz emd_37742.map.gz | 483.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-37742-v30.xml emd-37742-v30.xml emd-37742.xml emd-37742.xml | 21 KB 21 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_37742.png emd_37742.png | 75.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-37742.cif.gz emd-37742.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_37742_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37742_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37742_half_map_2.map.gz emd_37742_half_map_2.map.gz | 475.8 MB 475.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37742 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37742 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37742 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37742 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_37742_validation.pdf.gz emd_37742_validation.pdf.gz | 943.1 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_37742_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_37742_full_validation.pdf.gz | 942.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_37742_validation.xml.gz emd_37742_validation.xml.gz | 18.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_37742_validation.cif.gz emd_37742_validation.cif.gz | 22.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-37742 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-37742 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-37742 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-37742 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8wqeMC  8wqaC  8wqbC  8wqcC  8wqdC  8wqfC  8wqgC  8wqhC  8wqiC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_37742.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_37742.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
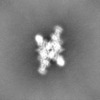
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.82 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_37742_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
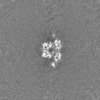
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
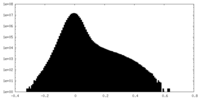
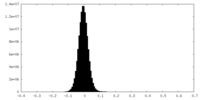
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_37742_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
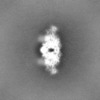
| ||||||||||||
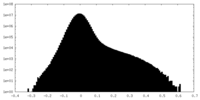
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cryo-EM structure of CUL2-RBX1-ELOB-ELOC-FEM1B bound with the C-d...
| Entire | Name: Cryo-EM structure of CUL2-RBX1-ELOB-ELOC-FEM1B bound with the C-degron of CUX1 (conformation 1) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM structure of CUL2-RBX1-ELOB-ELOC-FEM1B bound with the C-d...
| Supramolecule | Name: Cryo-EM structure of CUL2-RBX1-ELOB-ELOC-FEM1B bound with the C-degron of CUX1 (conformation 1) type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#6 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Cullin-2
| Macromolecule | Name: Cullin-2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 87.11475 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SASWSHPQFE KGGGSGGGSG TSLKPRVVDF DETWNKLLTT IKAVVMLEYV ERATWNDRFS DIYALCVAYP EPLGERLYTE TKIFLENHV RHLHKRVLES EEQVLVMYHR YWEEYSKGAD YMDCLYRYLN TQFIKKNGGG PLMEIGELAL DMWRKLMVEP L QAILIRML ...String: SASWSHPQFE KGGGSGGGSG TSLKPRVVDF DETWNKLLTT IKAVVMLEYV ERATWNDRFS DIYALCVAYP EPLGERLYTE TKIFLENHV RHLHKRVLES EEQVLVMYHR YWEEYSKGAD YMDCLYRYLN TQFIKKNGGG PLMEIGELAL DMWRKLMVEP L QAILIRML LREIKNDRGG EDPNQKVIHG VINSFVHVEQ YKKKFPLKFY QEIFESPFLT ETGEYYKQEA SNLLQESNCS QY MEKVLGR LKDEEIRCRK YLHPSSYTKV IHECQQRMVA DHLQFLHAEC HNIIRQEKKN DMANMYVLLR AVSTGLPHMI QEL QNHIHD EGLRATSNLT QENMPTLFVE SVLEVHGKFV QLINTVLNGD QHFMSALDKA LTSVVNYREP KSVCKAPELL AKYC DNLLK KSAKGMTENE VEDRLTSFIT VFKYIDDKDV FQKFYARMLA KRLIHGLSMS MDSEEAMINK LKQACGYEFT SKLHR MYTD MSVSADLNNK FNNFIKNQDT VIDLGISFQI YVLQAGAWPL TQAPSSTFAI PQELEKSVQM FELFYSQHFS GRKLTW LHY LCTGEVKMNY LGKPYVAMVT TYQMAVLLAF NNSETVSYKE LQDSTQMNEK ELTKTIKSLL DVKMINHDSE KEDIDAE SS FSLNMNFSSK RTKFKITTSM QKDTPQEMEQ TRSAVDEDRK MYLQAAIVRI MKARKVLRHN ALIQEVISQS RARFNPSI S MIKKCIEVLI DKQYIERSQA SADEYSYVA UniProtKB: Cullin-2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Protein fem-1 homolog B
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein fem-1 homolog B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 70.355062 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MEGLAGYVYK AASEGKVLTL AALLLNRSES DIRYLLGYVS QQGGQRSTPL IIAARNGHAK VVRLLLEHYR VQTQQTGTVR FDGYVIDGA TALWCAAGAG HFEVVKLLVS HGANVNHTTV TNSTPLRAAC FDGRLDIVKY LVENNANISI ANKYDNTCLM I AAYKGHTD ...String: MEGLAGYVYK AASEGKVLTL AALLLNRSES DIRYLLGYVS QQGGQRSTPL IIAARNGHAK VVRLLLEHYR VQTQQTGTVR FDGYVIDGA TALWCAAGAG HFEVVKLLVS HGANVNHTTV TNSTPLRAAC FDGRLDIVKY LVENNANISI ANKYDNTCLM I AAYKGHTD VVRYLLEQRA DPNAKAHCGA TALHFAAEAG HIDIVKELIK WRAAIVVNGH GMTPLKVAAE SCKADVVELL LS HADCDRR SRIEALELLG ASFANDRENY DIIKTYHYLY LAMLERFQDG DNILEKEVLP PIHAYGNRTE CRNPQELESI RQD RDALHM EGLIVRERIL GADNIDVSHP IIYRGAVYAD NMEFEQCIKL WLHALHLRQK GNRNTHKDLL RFAQVFSQMI HLNE TVKAP DIECVLRCSV LEIEQSMNRV KNISDADVHN AMDNYECNLY TFLYLVCIST KTQCSEEDQC KINKQIYNLI HLDPR TREG FTLLHLAVNS NTPVDDFHTN DVCSFPNALV TKLLLDCGAE VNAVDNEGNS ALHIIVQYNR PISDFLTLHS IIISLV EAG AHTDMTNKQN KTPLDKSTTG VSEILLKTQM KMSLKCLAAR AVRANDINYQ DQIPRTLEEF VGFH UniProtKB: Protein fem-1 homolog B |
-Macromolecule #3: Elongin-C
| Macromolecule | Name: Elongin-C / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10.84342 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MYVKLISSDG HEFIVKREHA LTSGTIKAML SGPGQFAENE TNEVNFREIP SHVLSKVCMY FTYKVRYTNS STEIPEFPIA PEIALELLM AANFLDC UniProtKB: Elongin-C |
-Macromolecule #4: Elongin-B
| Macromolecule | Name: Elongin-B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.147781 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDVFLMIRRH KTTIFTDAKE SSTVFELKRI VEGILKRPPD EQRLYKDDQL LDDGKTLGEC GFTSQTARPQ APATVGLAFR ADDTFEALC IEPFSSPPEL PDVMKPQDSG SSANEQAVQ UniProtKB: Elongin-B |
-Macromolecule #5: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1, N-terminally processed
| Macromolecule | Name: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1, N-terminally processed type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.19683 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SHMGAGKKRF EVKKWNAVAL WAWDIVVDNC AICRNHIMDL CIECQANQAS ATSEECTVAW GVCNHAFHFH CISRWLKTRQ VCPLDNREW EFQKYGH UniProtKB: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1 |
-Macromolecule #6: Protein CASP
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein CASP / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 3.143281 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GGGSGGGSKF ADHLHKFHEN DNGAAAGDLW Q UniProtKB: Protein CASP |
-Macromolecule #7: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 8112 / Average electron dose: 57.6 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.9 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.38 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 252311 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)