+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of human alpha-2/delta-1 with mirogabalin | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | gabapentinoid / Cache domain / cryo-EM / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / calcium ion transport into cytosol / regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / neuronal dense core vesicle ...regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / calcium ion transport into cytosol / regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / neuronal dense core vesicle / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / regulation of calcium ion transport / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane / sarcoplasmic reticulum / GABA-ergic synapse / cellular response to amyloid-beta / calcium ion transport / extracellular exosome / metal ion binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
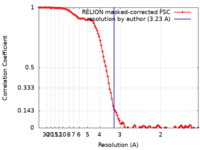
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.23 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kozai D / Numoto N / Fujiyoshi Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 2 items Japan, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: Recognition Mechanism of a Novel Gabapentinoid Drug, Mirogabalin, for Recombinant Human αδ1, a Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel Subunit. Authors: Daisuke Kozai / Nobutaka Numoto / Kouki Nishikawa / Akiko Kamegawa / Shohei Kawasaki / Yoko Hiroaki / Katsumasa Irie / Atsunori Oshima / Hiroyuki Hanzawa / Kousei Shimada / Yutaka Kitano / Yoshinori Fujiyoshi /  Abstract: Mirogabalin is a novel gabapentinoid drug with a hydrophobic bicyclo substituent on the γ-aminobutyric acid moiety that targets the voltage-gated calcium channel subunit αδ1. Here, to reveal the ...Mirogabalin is a novel gabapentinoid drug with a hydrophobic bicyclo substituent on the γ-aminobutyric acid moiety that targets the voltage-gated calcium channel subunit αδ1. Here, to reveal the mirogabalin recognition mechanisms of αδ1, we present structures of recombinant human αδ1 with and without mirogabalin analyzed by cryo-electron microscopy. These structures show the binding of mirogabalin to the previously reported gabapentinoid binding site, which is the extracellular dCache_1 domain containing a conserved amino acid binding motif. A slight conformational change occurs around the residues positioned close to the hydrophobic group of mirogabalin. Mutagenesis binding assays identified that residues in the hydrophobic interaction region, in addition to several amino acid binding motif residues around the amino and carboxyl groups of mirogabalin, are critical for mirogabalin binding. The A215L mutation introduced to decrease the hydrophobic pocket volume predictably suppressed mirogabalin binding and promoted the binding of another ligand, L-Leu, with a smaller hydrophobic substituent than mirogabalin. Alterations of residues in the hydrophobic interaction region of αδ1 to those of the αδ2, αδ3, and αδ4 isoforms, of which αδ3 and αδ4 are gabapentin-insensitive, suppressed the binding of mirogabalin. These results support the importance of hydrophobic interactions in αδ1 ligand recognition. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_35399.map.gz emd_35399.map.gz | 25.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-35399-v30.xml emd-35399-v30.xml emd-35399.xml emd-35399.xml | 16.5 KB 16.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_35399_fsc.xml emd_35399_fsc.xml | 10.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
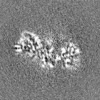
| Images |  emd_35399.png emd_35399.png | 131.2 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_35399_msk_1.map emd_35399_msk_1.map | 27.9 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-35399.cif.gz emd-35399.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_35399_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35399_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35399_half_map_2.map.gz emd_35399_half_map_2.map.gz | 25.8 MB 25.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35399 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35399 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35399 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35399 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_35399_validation.pdf.gz emd_35399_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_35399_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_35399_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_35399_validation.xml.gz emd_35399_validation.xml.gz | 15.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_35399_validation.cif.gz emd_35399_validation.cif.gz | 20.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35399 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35399 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35399 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35399 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8if3MC  8if4C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_35399.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 27.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_35399.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 27.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.765 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
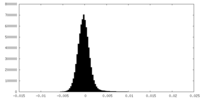
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_35399_msk_1.map emd_35399_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
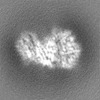
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
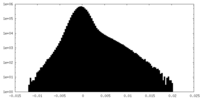
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_35399_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_35399_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1
| Entire | Name: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1
| Supramolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 140 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 124.413062 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAAGCLLALT LTLFQSLLIG PSSEEPFPSA VTIKSWVDKM QEDLVTLAKT ASGVNQLVDI YEKYQDLYTV EPNNARQLVE IAARDIEKL LSNRSKALVR LALEAEKVQA AHQWREDFAS NEVVYYNAKD DLDPEKNDSE PGSQRIKPVF IEDANFGRQI S YQHAAVHI ...String: MAAGCLLALT LTLFQSLLIG PSSEEPFPSA VTIKSWVDKM QEDLVTLAKT ASGVNQLVDI YEKYQDLYTV EPNNARQLVE IAARDIEKL LSNRSKALVR LALEAEKVQA AHQWREDFAS NEVVYYNAKD DLDPEKNDSE PGSQRIKPVF IEDANFGRQI S YQHAAVHI PTDIYEGSTI VLNELNWTSA LDEVFKKNRE EDPSLLWQVF GSATGLARYY PASPWVDNSR TPNKIDLYDV RR RPWYIQG AASPKDMLIL VDVSGSVSGL TLKLIRTSVS EMLETLSDDD FVNVASFNSN AQDVSCFQHL VQANVRNKKV LKD AVNNIT AKGITDYKKG FSFAFEQLLN YNVSRANCNK IIMLFTDGGE ERAQEIFNKY NKDKKVRVFT FSVGQHNYDR GPIQ WMACE NKGYYYEIPS IGAIRINTQE YLDVLGRPMV LAGDKAKQVQ WTNVYLDALE LGLVITGTLP VFNITGQFEN KTNLK NQLI LGVMGVDVSL EDIKRLTPRF TLCPNGYYFA IDPNGYVLLH PNLQPKNPKS QEPVTLDFLD AELENDIKVE IRNKMI DGE SGEKTFRTLV KSQDERYIDK GNRTYTWTPV NGTDYSLALV LPTYSFYYIK AKLEETITQA RSKKGKMKDS ETLKPDN FE ESGYTFIAPR DYCNDLKISD NNTEFLLNFN EFIDRHHHHH HHHKTPNNPS CNADLINRVL LDAGFTNELV QNYWSKQK N IKGVKARFVV TDGGITRVYP KEAGENWQEN PETYEDSFYK RSLDNDNYVF TAPYFNKSGP GAYESGIMVS KAVEIYIQG KLLKPAVVGI KIDVNSWIEN FTKTSIRDPC AGPVCDCKRN SDVMDCVILD DGGFLLMANH DDYTNQIGRF FGEIDPSLMR HLVNISVYA FNKSYDYQSV CEPGAAPKQG AGHRSAYVPS VADILQIGWW ATAAAWSILQ QFLLSLTFPR LLEAVEMEDD D FTASLSKQ SCITEQTQYF FDNDSKSFSG VLDCGNCSRI FHGEKLMNTN LIFIMVESKG TCPCDTRLLI QAEQTSDGPN PC DMVKQPR YRKGPDVCFD NNVLEDYTDC GGVSGLNPSL WYIIGIQFLL LWLVSGSTHR LL UniProtKB: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 |
-Macromolecule #3: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 7 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #4: 2-[(1R,5S,6S)-6-(aminomethyl)-3-ethyl-6-bicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-enyl...
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-[(1R,5S,6S)-6-(aminomethyl)-3-ethyl-6-bicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-enyl]acetic acid type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: 8X9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 209.285 Da |
| Chemical component information | 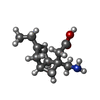 ChemComp-8X9: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL CRYO ARM 300 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 68.3 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)