+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3534 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
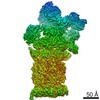
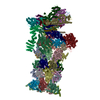
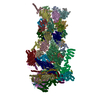
| Title | 26S proteasome in presence of ATP (s1) | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Macromolecular complex / 26S proteasome / Protease / Hydrolase | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationSAGA complex localization to transcription regulatory region / Metalloprotease DUBs / peroxisome fission / proteasome storage granule assembly / proteasome regulatory particle assembly / transcription export complex 2 / protein deneddylation / maintenance of DNA trinucleotide repeats / filamentous growth / COP9 signalosome ...SAGA complex localization to transcription regulatory region / Metalloprotease DUBs / peroxisome fission / proteasome storage granule assembly / proteasome regulatory particle assembly / transcription export complex 2 / protein deneddylation / maintenance of DNA trinucleotide repeats / filamentous growth / COP9 signalosome / cytosolic proteasome complex / proteasome regulatory particle / protein-containing complex localization / proteasome regulatory particle, lid subcomplex / proteasome-activating activity / mitochondrial fission / proteasome regulatory particle, base subcomplex / metal-dependent deubiquitinase activity / K48-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / proteasome core complex assembly / nuclear outer membrane-endoplasmic reticulum membrane network / Proteasome assembly / Cross-presentation of soluble exogenous antigens (endosomes) / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / proteasomal ubiquitin-independent protein catabolic process / nonfunctional rRNA decay / Ubiquitin Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / Regulation of PTEN stability and activity / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / peptide catabolic process / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / Neddylation / proteasome binding / Orc1 removal from chromatin / regulation of protein catabolic process / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / proteasome storage granule / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / protein deubiquitination / positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / endopeptidase activator activity / proteasome assembly / Ub-specific processing proteases / proteasome endopeptidase complex / proteasome core complex, beta-subunit complex / threonine-type endopeptidase activity / proteasome core complex, alpha-subunit complex / mRNA export from nucleus / enzyme regulator activity / ERAD pathway / Neutrophil degranulation / protein folding chaperone / proteasome complex / ubiquitin binding / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / nucleotide-excision repair / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / metallopeptidase activity / peroxisome / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / endopeptidase activity / molecular adaptor activity / ubiquitinyl hydrolase 1 / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / cysteine-type deubiquitinase activity / regulation of cell cycle / chromatin remodeling / protein domain specific binding / mRNA binding / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / structural molecule activity / endoplasmic reticulum / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / ATP hydrolysis activity / mitochondrion / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / metal ion binding / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.1 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wehmer M / Rudack T | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, Germany,  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2017 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2017Title: Structural insights into the functional cycle of the ATPase module of the 26S proteasome. Authors: Marc Wehmer / Till Rudack / Florian Beck / Antje Aufderheide / Günter Pfeifer / Jürgen M Plitzko / Friedrich Förster / Klaus Schulten / Wolfgang Baumeister / Eri Sakata /    Abstract: In eukaryotic cells, the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is responsible for the regulated degradation of intracellular proteins. The 26S holocomplex comprises the core particle (CP), where ...In eukaryotic cells, the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is responsible for the regulated degradation of intracellular proteins. The 26S holocomplex comprises the core particle (CP), where proteolysis takes place, and one or two regulatory particles (RPs). The base of the RP is formed by a heterohexameric AAA ATPase module, which unfolds and translocates substrates into the CP. Applying single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and image classification to samples in the presence of different nucleotides and nucleotide analogs, we were able to observe four distinct conformational states (s1 to s4). The resolution of the four conformers allowed for the construction of atomic models of the AAA ATPase module as it progresses through the functional cycle. In a hitherto unobserved state (s4), the gate controlling access to the CP is open. The structures described in this study allow us to put forward a model for the 26S functional cycle driven by ATP hydrolysis. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3534.map.gz emd_3534.map.gz | 202.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3534-v30.xml emd-3534-v30.xml emd-3534.xml emd-3534.xml | 36.2 KB 36.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_3534.png emd_3534.png | 54.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-3534.cif.gz emd-3534.cif.gz | 9.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3534 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3534 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3534 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3534 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_3534_validation.pdf.gz emd_3534_validation.pdf.gz | 280.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_3534_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_3534_full_validation.pdf.gz | 280 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_3534_validation.xml.gz emd_3534_validation.xml.gz | 6.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3534 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3534 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3534 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3534 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5mp9MC  5mpdMC  6fvtM  3535C 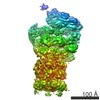 3536C 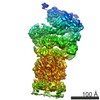 3537C 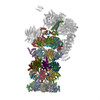 5mpaC  5mpbC  5mpcC  5mpeC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3534.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3534.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.38 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
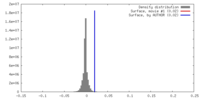
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : 26S proteasome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in presence of ATP (s1)
+Supramolecule #1: 26S proteasome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in presence of ATP (s1)
+Macromolecule #1: Proteasome subunit alpha type-1
+Macromolecule #2: Proteasome subunit alpha type-2
+Macromolecule #3: Proteasome subunit alpha type-3
+Macromolecule #4: Proteasome subunit alpha type-4
+Macromolecule #5: Proteasome subunit alpha type-5
+Macromolecule #6: Proteasome subunit alpha type-6
+Macromolecule #7: Probable proteasome subunit alpha type-7
+Macromolecule #8: Proteasome subunit beta type-1
+Macromolecule #9: Proteasome subunit beta type-2
+Macromolecule #10: Proteasome subunit beta type-3
+Macromolecule #11: Proteasome subunit beta type-4
+Macromolecule #12: Proteasome subunit beta type-5
+Macromolecule #13: Proteasome subunit beta type-6
+Macromolecule #14: Proteasome subunit beta type-7
+Macromolecule #15: 26S protease regulatory subunit 7 homolog
+Macromolecule #16: 26S protease regulatory subunit 4 homolog
+Macromolecule #17: 26S protease regulatory subunit 6B homolog
+Macromolecule #18: 26S protease subunit RPT4
+Macromolecule #19: 26S protease regulatory subunit 6A
+Macromolecule #20: 26S protease regulatory subunit 8 homolog
+Macromolecule #21: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #22: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #23: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Grid | Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 15 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average exposure time: 10.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 45.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 1.4) / Number images used: 286500 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 1.4) |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 1.4) |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




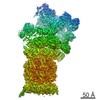
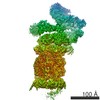
























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)